Essential function of dynamin in the invasive properties and actin architecture of v-Src induced podosomes/invadosomes
- PMID: 24348990
- PMCID: PMC3857171
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077956
Essential function of dynamin in the invasive properties and actin architecture of v-Src induced podosomes/invadosomes
Abstract
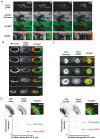
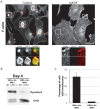
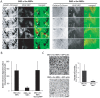
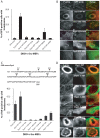
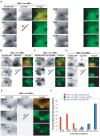
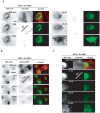
The large GTPase dynamin plays a key role in endocytosis but is also localized at numerous actin rich sites. We investigated dynamin functions at podosomes/invadosomes, actin-based cellular adhesion structures implicated in tissue invasion. Podosomes/invadosomes are constituted of long F-actin bundles perpendicular to the substratum (actin cores), connected to randomly arranged F-actin fibers parallel to the substratum (actin cloud). We show here that dynamin depletion in v-Src-transformed fibroblasts triggers a massive disorganization of podosomes/invadosomes (isolated or in rosettes), with a corresponding inhibition of their invasive properties. The action of dynamin at podosomes/invadosomes requires a functional full-length protein, suggesting that the effects of dynamin at these sites and in membrane remodelling during endocytosis are mediated by similar mechanisms. In order to determine direct effect of dynamin depletion on invadosome, an optogenetic approach based on the photosensitizer KillerRed was developed. Acute dynamin photo-inactivation leads to a very rapid disorganization of invadosome without affecting focal adhesions. Dynamin therefore is a key regulator of the architecture of actin in podosomes/invadosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamin forms a Src kinase-sensitive complex with Cbl and regulates podosomes and osteoclast activity.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3301-13. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1117. Epub 2005 May 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15872089 Free PMC article.
-
A functional link between dynamin and the actin cytoskeleton at podosomes.J Cell Biol. 2000 Jul 24;150(2):377-89. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.2.377. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10908579 Free PMC article.
-
Tks5 and Dynamin-2 enhance actin bundle rigidity in invadosomes to promote myoblast fusion.J Cell Biol. 2019 May 6;218(5):1670-1685. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201809161. Epub 2019 Mar 20. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30894403 Free PMC article.
-
Probing invadosomes: technologies for the analysis of invadosomes.FEBS J. 2022 Oct;289(19):5850-5863. doi: 10.1111/febs.16098. Epub 2021 Jul 12. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34196119 Review.
-
Significance of kinase activity in the dynamic invadosome.Eur J Cell Biol. 2016 Nov;95(11):483-492. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Eur J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27465307 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamin and endocytosis are required for the fusion of osteoclasts and myoblasts.J Cell Biol. 2014 Oct 13;207(1):73-89. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201401137. Epub 2014 Oct 6. J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25287300 Free PMC article.
-
Late stages of the synchronized macrophage fusion in osteoclast formation depend on dynamin.Biochem J. 2014 Dec 15;464(3):293-300. doi: 10.1042/BJ20141233. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 25336256 Free PMC article.
-
Tks5 SH3 domains exhibit differential effects on invadopodia development.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 30;15(1):e0227855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227855. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31999741 Free PMC article.
-
Sorting nexin 9 negatively regulates invadopodia formation and function in cancer cells.J Cell Sci. 2016 Jul 15;129(14):2804-16. doi: 10.1242/jcs.188045. Epub 2016 Jun 8. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27278018 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamin2 controls Rap1 activation and integrin clustering in human T lymphocyte adhesion.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 8;12(3):e0172443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172443. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28273099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McMahon HT, Boucrot E (2011) Molecular mechanism and physiological functions of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12: 517–533. - PubMed
-
- Schmid SL, Frolov VA (2011) Dynamin: functional design of a membrane fission catalyst. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27: 79–105. - PubMed
-
- Schafer DA (2004) Regulating actin dynamics at membranes: a focus on dynamin. Traffic 5: 463–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR042927/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE004724/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA046128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R37 DE004724/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- DK45735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA46128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036251/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DA018343/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AR-42927/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS36251/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS036251/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DE-04724/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA018343/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

