TOR-centric view on insulin resistance and diabetic complications: perspective for endocrinologists and gerontologists
- PMID: 24336084
- PMCID: PMC3877573
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.506
TOR-centric view on insulin resistance and diabetic complications: perspective for endocrinologists and gerontologists
Abstract
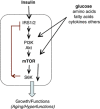
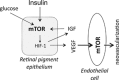
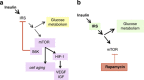
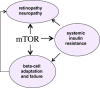
This article is addressed to endocrinologists treating patients with diabetic complications as well as to basic scientists studying an elusive link between diseases and aging. It answers some challenging questions. What is the link between insulin resistance (IR), cellular aging and diseases? Why complications such as retinopathy may paradoxically precede the onset of type II diabetes. Why intensive insulin therapy may initially worsen retinopathy. How nutrient- and insulin-sensing mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway can drive insulin resistance and diabetic complications. And how rapamycin, at rational doses and schedules, may prevent IR, retinopathy, nephropathy and beta-cell failure, without causing side effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapamycin-induced glucose intolerance: hunger or starvation diabetes.Cell Cycle. 2011 Dec 15;10(24):4217-24. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.24.18595. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 22157190
-
Effect of Shenzhu Tiaopi granule on hepatic insulin resistance in diabetic Goto-Kakizakirats via liver kinase B1/adenosine 5'-monophosphate/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2021 Feb;41(1):107-116. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2021.01.013. J Tradit Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 33522203
-
Fathoming the Role of mTOR in Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2023;16(5):520-529. doi: 10.2174/1874467215666221005123919. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36200157 Review.
-
From Diabetes to Diabetic Complications: Role of Autophagy.Curr Med Sci. 2023 Jun;43(3):434-444. doi: 10.1007/s11596-023-2727-4. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Curr Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37115396 Review.
-
Resistin promotes cardiac hypertrophy via the AMP-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin (AMPK/mTOR) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase/insulin receptor substrate 1 (JNK/IRS1) pathways.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 27;286(21):18465-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.200022. Epub 2011 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21478152 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Koschei the immortal and anti-aging drugs.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Dec 4;5(12):e1552. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.520. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25476900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geroconversion: irreversible step to cellular senescence.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(23):3628-35. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.985507. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25483060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc transporter Slc39a14 regulates inflammatory signaling associated with hypertrophic adiposity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Feb 15;310(4):E258-68. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00421.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26646099 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Syndrome and Neuroprotection.Front Neurosci. 2018 Apr 20;12:196. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00196. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29731703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating RNAs as predictive markers for the progression of type 2 diabetes.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Apr;23(4):2753-2768. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14182. Epub 2019 Feb 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30734465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Girach A, Vignati L. Diabetic microvascular complications--can the presence of one predict the development of another. J Diabetes Complications. 2006;20:228–237. - PubMed
-
- Harris MI, Klein R, Welborn TA, Knuiman MW. Onset of NIDDM occurs at least 4–7yr before clinical diagnosis. Diabetes Care. 1992;15:815–819. - PubMed
-
- Ellis JD, Zvandasara T, Leese G, McAlpine R, Macewen CJ, Baines PS, et al. Clues to duration of undiagnosed disease from retinopathy and maculopathy at diagnosis in type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011;95:1229–1233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

