Primary macrophages rely on histone deacetylase 1 and 2 expression to induce type I interferon in response to gammaherpesvirus infection
- PMID: 24335310
- PMCID: PMC3911555
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.03278-13
Primary macrophages rely on histone deacetylase 1 and 2 expression to induce type I interferon in response to gammaherpesvirus infection
Abstract
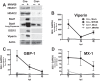
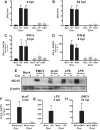
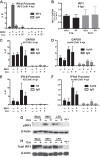
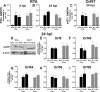
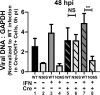
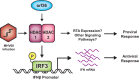
Type I interferon is induced shortly following viral infection and represents a first line of host defense against a majority of viral pathogens. Not surprisingly, both replication and latency of gammaherpesviruses, ubiquitous cancer-associated pathogens, are attenuated by type I interferon, although the mechanism of attenuation remains poorly characterized. Gammaherpesviruses also target histone deacetylases (HDACs), a family of pleiotropic enzymes that modify gene expression and several cell signaling pathways. Specifically, we have previously shown that a conserved gammaherpesvirus protein kinase interacts with HDAC1 and -2 to promote gammaherpesvirus replication in primary macrophages. In the current study, we have used genetic approaches to show that expression of HDAC1 and -2 is critical for induction of a type I interferon response following gammaherpesvirus infection of primary macrophages. Specifically, expression of HDAC1 and -2 was required for phosphorylation of interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and accumulation of IRF3 at the beta interferon promoter in gammaherpesvirus-infected primary macrophages. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of a specific role for HDAC1 and -2 in the induction of type I interferon responses in primary immune cells following virus infection. Furthermore, because HDAC1 and -2 are overexpressed in several types of cancer, our findings illuminate potential side effects of HDAC1- and -2-specific inhibitors that are currently under development as cancer therapy agents. IMPORTANCE Gammaherpesviruses establish chronic infection in a majority of the adult population and are associated with several malignancies. Infected cells counteract gammaherpesvirus infection via innate immune signaling mediated primarily through type I interferon. The induction of type I interferon expression proceeds through several stages using molecular mechanisms that are still incompletely characterized. In this study, we show that expression of HDAC1 and -2 by macrophages is required to mount a type I interferon response to incoming gammaherpesvirus. The involvement of HDAC1 and -2 in the type I interferon response highlights the pleiotropic roles of these enzymes in cellular signaling. Interestingly, HDAC1 and -2 are deregulated in cancer and are attractive targets of new cancer therapies. Due to the ubiquitous and chronic nature of gammaherpesvirus infection, the role of HDAC1 and -2 in the induction of type I interferon responses should be considered during the clinical development of HDAC1- and -2-specific inhibitors.
Figures
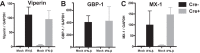
Similar articles
-
A conserved gammaherpesvirus protein kinase targets histone deacetylases 1 and 2 to facilitate viral replication in primary macrophages.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(13):7314-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02713-12. Epub 2013 Apr 24. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23616648 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon Regulatory Factor 1 and Type I Interferon Cooperate To Control Acute Gammaherpesvirus Infection.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01444-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01444-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795415 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Supports the Establishment of Chronic Gammaherpesvirus Infection in a Route- and Dose-Dependent Manner.J Virol. 2021 Apr 12;95(9):e02208-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02208-20. Print 2021 Apr 12. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33597211 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma interferon blocks gammaherpesvirus reactivation from latency in a cell type-specific manner.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):6134-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00108-07. Epub 2007 Mar 14. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17360749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 regulate DNA replication and DNA repair: potential targets for genome stability-mechanism-based therapeutics for a subset of cancers.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(12):1779-85. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1042634. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25942572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota-derived butyrate promotes coronavirus TGEV infection through impairing RIG-I-triggered local type I interferon responses via class I HDAC inhibition.J Virol. 2024 Feb 20;98(2):e0137723. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01377-23. Epub 2024 Jan 10. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38197629 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved Herpesvirus Kinase ORF36 Activates B2 Retrotransposons during Murine Gammaherpesvirus Infection.J Virol. 2020 Jul 1;94(14):e00262-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00262-20. Print 2020 Jul 1. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32404524 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of HDAC2 with SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 and IRF3 Is Not Required for NSP5-Mediated Inhibition of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0232222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02322-22. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36173315 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Monocyte and Macrophage Function.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Nov 10;25(14):758-774. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6695. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26983461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetylation in Tumor Immune Evasion Regulation.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 22;12:771588. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.771588. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34880761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

