RNA-seq differential expression studies: more sequence or more replication?
- PMID: 24319002
- PMCID: PMC3904521
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt688
RNA-seq differential expression studies: more sequence or more replication?
Abstract
Motivation: RNA-seq is replacing microarrays as the primary tool for gene expression studies. Many RNA-seq studies have used insufficient biological replicates, resulting in low statistical power and inefficient use of sequencing resources.
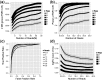
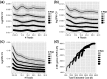
Results: We show the explicit trade-off between more biological replicates and deeper sequencing in increasing power to detect differentially expressed (DE) genes. In the human cell line MCF7, adding more sequencing depth after 10 M reads gives diminishing returns on power to detect DE genes, whereas adding biological replicates improves power significantly regardless of sequencing depth. We also propose a cost-effectiveness metric for guiding the design of large-scale RNA-seq DE studies. Our analysis showed that sequencing less reads and performing more biological replication is an effective strategy to increase power and accuracy in large-scale differential expression RNA-seq studies, and provided new insights into efficient experiment design of RNA-seq studies.
Availability and implementation: The code used in this paper is provided on: http://home.uchicago.edu/∼jiezhou/replication/. The expression data is deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus under the accession ID GSE51403.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Power analysis and sample size estimation for RNA-Seq differential expression.RNA. 2014 Nov;20(11):1684-96. doi: 10.1261/rna.046011.114. Epub 2014 Sep 22. RNA. 2014. PMID: 25246651 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical detection of differentially expressed genes based on RNA-seq: from biological to phylogenetic replicates.Brief Bioinform. 2016 Mar;17(2):243-8. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv035. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Brief Bioinform. 2016. PMID: 26108230 Review.
-
A flexible count data model to fit the wide diversity of expression profiles arising from extensively replicated RNA-seq experiments.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Aug 21;14:254. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-254. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23965047 Free PMC article.
-
Empirical assessment of the impact of sample number and read depth on RNA-Seq analysis workflow performance.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Nov 14;19(1):423. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2445-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30428853 Free PMC article.
-
The power and promise of RNA-seq in ecology and evolution.Mol Ecol. 2016 Mar;25(6):1224-41. doi: 10.1111/mec.13526. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Mol Ecol. 2016. PMID: 26756714 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and bioinformatics analysis of genome-wide CLIP experiments.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jun 23;43(11):5263-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv439. Epub 2015 May 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25958398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Candida pathogens induce protective mitochondria-associated type I interferon signalling and a damage-driven response in vaginal epithelial cells.Nat Microbiol. 2021 May;6(5):643-657. doi: 10.1038/s41564-021-00875-2. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Nat Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33753919
-
On taming the effect of transcript level intra-condition count variation during differential expression analysis: A story of dogs, foxes and wolves.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 22;17(9):e0274591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274591. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36136981 Free PMC article.
-
Truncated O-glycosylation in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer reveals a gene expression signature associated with extracellular matrix and proteolysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 20;14(1):1809. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52204-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38245559 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lactic acid bacteria-fermented formula milk supplementation on ileal microbiota, transcriptomic profile, and mucosal immunity in weaned piglets.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 6;13(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s40104-022-00762-8. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36199127 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

