Transposon mutagenesis identifies genes driving hepatocellular carcinoma in a chronic hepatitis B mouse model
- PMID: 24316982
- PMCID: PMC4131144
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2847
Transposon mutagenesis identifies genes driving hepatocellular carcinoma in a chronic hepatitis B mouse model
Abstract
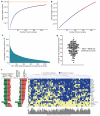
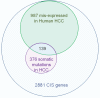
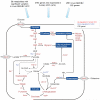
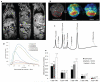
The most common risk factor for developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV). To better understand the evolutionary forces driving HCC, we performed a near-saturating transposon mutagenesis screen in a mouse HBV model of HCC. This screen identified 21 candidate early stage drivers and a very large number (2,860) of candidate later stage drivers that were enriched for genes that are mutated, deregulated or functioning in signaling pathways important for human HCC, with a striking 1,199 genes being linked to cellular metabolic processes. Our study provides a comprehensive overview of the genetic landscape of HCC.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transposon mouse models to elucidate the genetic mechanisms of hepatitis B viral induced hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 14;21(42):12157-70. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12157. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26576100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transposon mutagenesis identifies genes and cellular processes driving epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jun 14;113(24):E3384-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606876113. Epub 2016 May 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27247392 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular profiling of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma using SB transposon mutagenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 30;115(44):E10417-E10426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1808968115. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30327349 Free PMC article.
-
Sleeping Beauty Insertional Mutagenesis in Mice Identifies Drivers of Steatosis-Associated Hepatic Tumors.Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 1;77(23):6576-6588. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2281. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28993411 Free PMC article.
-
Conceptual models for the initiation of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.Liver Int. 2015 Jul;35(7):1786-800. doi: 10.1111/liv.12773. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25640596 Review.
Cited by
-
NOTCH1 activation compensates BRCA1 deficiency and promotes triple-negative breast cancer formation.Nat Commun. 2020 Jun 26;11(1):3256. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16936-9. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32591500 Free PMC article.
-
Sleeping Beauty Mouse Models of Cancer: Microenvironmental Influences on Cancer Genetics.Front Oncol. 2019 Jul 9;9:611. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00611. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31338332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically Engineered Mouse Models of Gliomas: Technological Developments for Translational Discoveries.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 9;11(9):1335. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091335. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31505839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRTFB suppresses colorectal cancer development through regulating SPDL1 and MCAM.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Nov 19;116(47):23625-23635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1910413116. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31690663 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA binding proteins LARP4A and LARP4B promote sarcoma and carcinoma growth and metastasis.iScience. 2024 Feb 24;27(4):109288. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109288. eCollection 2024 Apr 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38532886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imbeaud S, Ladeiro Y, Zucman-Rossi J. Identification of novel oncogenes and tumor suppressors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30:75–86. - PubMed
-
- Wurmbach E, et al. Genome-wide molecular profiles of HCV-induced dysplasia and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2007;45:938–947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

