Asymmetrical Fc engineering greatly enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) effector function and stability of the modified antibodies
- PMID: 24311787
- PMCID: PMC3916558
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.513366
Asymmetrical Fc engineering greatly enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) effector function and stability of the modified antibodies
Abstract
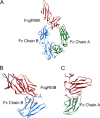
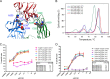
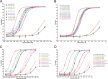
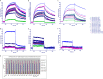
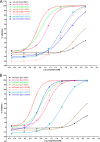
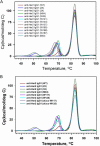
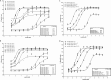
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) is mediated through the engagement of the Fc segment of antibodies with Fcγ receptors (FcγRs) on immune cells upon binding of tumor or viral antigen. The co-crystal structure of FcγRIII in complex with Fc revealed that Fc binds to FcγRIII asymmetrically with two Fc chains contacting separate regions of the FcγRIII by utilizing different residues. To fully explore this asymmetrical nature of the Fc-FcγR interaction, we screened more than 9,000 individual clones in Fc heterodimer format in which different mutations were introduced at the same position of two Fc chains using a high throughput competition AlphaLISA® assay. To this end, we have identified a panel of novel Fc variants with significant binding improvement to FcγRIIIA (both Phe-158 and Val-158 allotypes), increased ADCC activity in vitro, and strong tumor growth inhibition in mice xenograft human tumor models. Compared with previously identified Fc variants in conventional IgG format, Fc heterodimers with asymmetrical mutations can achieve similar or superior potency in ADCC-mediated tumor cell killing and demonstrate improved stability in the CH2 domain. Fc heterodimers also allow more selectivity toward activating FcγRIIA than inhibitory FcγRIIB. Afucosylation of Fc variants further increases the affinity of Fc to FcγRIIIA, leading to much higher ADCC activity. The discovery of these Fc variants will potentially open up new opportunities of building the next generation of therapeutic antibodies with enhanced ADCC effector function for the treatment of cancers and infectious diseases.
Keywords: Antibody Engineering; Cancer Therapy; Cell Death; FCγ Receptors; NK Cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of a novel asymmetrically engineered Fc variant with improved affinity for FcγRs.Mol Immunol. 2014 Mar;58(1):132-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.11.017. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24334029
-
Increasing FcγRIIa affinity of an FcγRIII-optimized anti-EGFR antibody restores neutrophil-mediated cytotoxicity.MAbs. 2014 Mar-Apr;6(2):409-21. doi: 10.4161/mabs.27457. Epub 2013 Dec 11. MAbs. 2014. PMID: 24492248 Free PMC article.
-
An Fc engineering approach that modulates antibody-dependent cytokine release without altering cell-killing functions.MAbs. 2015;7(3):494-504. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1022692. MAbs. 2015. PMID: 25933349 Free PMC article.
-
The "less-is-more" in therapeutic antibodies: Afucosylated anti-cancer antibodies with enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.MAbs. 2018 Jul;10(5):693-711. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1466767. MAbs. 2018. PMID: 29733746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Fcγ receptors in HER2-targeted breast cancer therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Jan;10(1):e003171. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003171. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34992090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A perspective on the structure and receptor binding properties of immunoglobulin G Fc.Biochemistry. 2015 May 19;54(19):2931-42. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00299. Epub 2015 May 7. Biochemistry. 2015. PMID: 25926001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered bispecific antibodies targeting the interleukin-6 and -8 receptors potently inhibit cancer cell migration and tumor metastasis.Mol Ther. 2022 Nov 2;30(11):3430-3449. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.07.008. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35841152 Free PMC article.
-
Fc receptors and their influence on efficacy of therapeutic antibodies for treatment of viral diseases.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015;13(11):1351-60. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2015.1079127. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015. PMID: 26466016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Antibody Design.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2015;17:191-216. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071114-040733. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2015. PMID: 26274600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asymmetric Fc Engineering for Bispecific Antibodies with Reduced Effector Function.Antibodies (Basel). 2017 May 16;6(2):7. doi: 10.3390/antib6020007. Antibodies (Basel). 2017. PMID: 31548523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reichert J. M., Valge-Archer V. E. (2007) Development trends for monoclonal antibody cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 6, 349–356 - PubMed
-
- Nimmerjahn F., Ravetch J. V. (2008) Fcγ receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 34–47 - PubMed
-
- Gessner J. E., Heiken H., Tamm A., Schmidt R. E. (1998) The IgG Fc receptor family. Ann. Hematol. 76, 231–248 - PubMed
-
- Cartron G., Dacheux L., Salles G., Solal-Celigny P., Bardos P., Colombat P., Watier H. (2002) Therapeutic activity of humanized ant-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcγRIIIa gene. Blood 99, 754–758 - PubMed
-
- Musolino A., Naldi N., Bortesi B., Pezzuolo D., Capelletti M., Missale G., Laccabue D., Zerbini A., Camisa R., Bisagni G., Neri T. M., Ardizzoni A. (2008) Immunoglobin G fragment C receptor polymorphisms and clinical efficacy of trastuzumab-based therapy in patients with Her-2/neu-positive metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 1789–1796 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

