cAMP responsive element modulator (CREM) α mediates chromatin remodeling of CD8 during the generation of CD3+ CD4- CD8- T cells
- PMID: 24297179
- PMCID: PMC3900979
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.523605
cAMP responsive element modulator (CREM) α mediates chromatin remodeling of CD8 during the generation of CD3+ CD4- CD8- T cells
Abstract
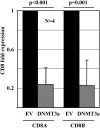
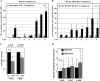
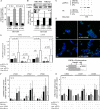
TCR-αβ(+)CD3(+)CD4(-)CD8(-) "double negative" T cells are expanded in the peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus-prone mice. Double negative T cells have been claimed to derive from CD8(+) cells that down-regulate CD8 co-receptors and acquire a distinct effector phenotype that includes the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. This, along with the fact that double negative T cells have been documented in inflamed organs, suggests that they may contribute to disease expression and tissue damage. We recently linked the transcription factor cAMP responsive element modulator (CREM) α, which is expressed at increased levels in T cells from SLE patients and lupus prone MRL/lpr mice, with trans-repression of a region syntenic to the murine CD8b promoter. However, the exact molecular mechanisms that result in a stable silencing of both CD8A and CD8B genes remain elusive. Here, we demonstrate that CREMα orchestrates epigenetic remodeling of the CD8 cluster through the recruitment of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) 3a and histone methyltransferase G9a. Thus, we propose that CREMα is essential for the expansion of double negative T cells in SLE. CREMα blockade may have therapeutic value in autoimmune disorders with DN T cell expansion.
Keywords: CD8; CREMα; Chromatin; Chromatin Histone Modification; DNA Methylation; Double Negative T Cells; Epigenetics; Histone Methylation; Histone Modification; SLE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
cAMP-responsive element modulator α (CREMα) trans-represses the transmembrane glycoprotein CD8 and contributes to the generation of CD3+CD4-CD8- T cells in health and disease.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 1;288(44):31880-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.508655. Epub 2013 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24047902 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM)α protein induces interleukin 17A expression and mediates epigenetic alterations at the interleukin-17A gene locus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 16;286(50):43437-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.299313. Epub 2011 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22025620 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM)α protein signaling mediates epigenetic remodeling of the human interleukin-2 gene: implications in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 16;286(50):43429-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.299339. Epub 2011 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21976679 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP responsive element modulator α promotes effector T cells in systemic autoimmune diseases.Immunology. 2023 Dec;170(4):470-482. doi: 10.1111/imm.13680. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Immunology. 2023. PMID: 37435993 Review.
-
cAMP responsive element modulator: a critical regulator of cytokine production.Trends Mol Med. 2013 Apr;19(4):262-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Trends Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23491535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA methylation in systemic lupus erythematosus.Epigenomics. 2017 Apr;9(4):505-525. doi: 10.2217/epi-2016-0096. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Epigenomics. 2017. PMID: 27885845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic AMP Response Element Modulator-α Suppresses PD-1 Expression and Promotes Effector CD4+ T Cells in Psoriasis.J Immunol. 2021 Jul 1;207(1):55-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100240. Epub 2021 Jun 16. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34135066 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of T cell differentiation and function by epigenetic modification enzymes.Semin Immunopathol. 2019 May;41(3):315-326. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00731-w. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Semin Immunopathol. 2019. PMID: 30963214 Review.
-
Double-negative T resident memory cells of the lung react to influenza virus infection via CD11c(hi) dendritic cells.Mucosal Immunol. 2016 Jul;9(4):999-1014. doi: 10.1038/mi.2015.91. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Mucosal Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26376363
-
Effects of Major Epigenetic Factors on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Iran Biomed J. 2018 Sep;22(5):294-302. doi: 10.29252/ibj.22.5.294. Epub 2018 May 27. Iran Biomed J. 2018. PMID: 29803202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hedrich C. M., Rauen T., Crispin J. C., Koga T., Ioannidis C., Zajdel M., Kyttaris V. C., Tsokos G. C. (2013) cAMP responsive element modulator (CREM)α trans-represses the transmembrane glycoprotein CD8 and contributes to the generation of CD3+CD4−CD8− T cells in health and disease. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 31880–31887 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hostert A., Tolaini M., Festenstein R., McNeill L., Malissen B., Williams O., Zamoyska R., Kioussis D. (1997) A CD8 genomic fragment that directs subset-specific expression of CD8 in transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 158, 4270–4281 - PubMed
-
- Kieffer L. J., Yan L., Hanke J. H., Kavathas P. B. (1997) Appropriate developmental expression of human CD8β in transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 159, 4907–4912 - PubMed
-
- Kioussis D., Ellmeier W. (2002) Chromatin and CD4, CD8A and CD8B gene expression during thymic differentiation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 909–919 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

