Hrs- and CD63-dependent competing mechanisms make different sized endosomal intraluminal vesicles
- PMID: 24279430
- PMCID: PMC4253088
- DOI: 10.1111/tra.12139
Hrs- and CD63-dependent competing mechanisms make different sized endosomal intraluminal vesicles
Abstract
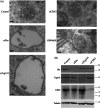
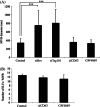
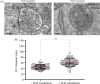
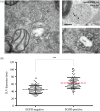
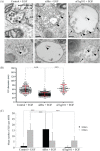
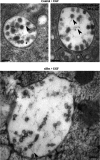
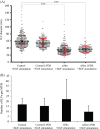
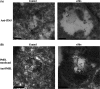
Multivesicular endosomes/bodies (MVBs) contain intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that bud away from the cytoplasm. Multiple mechanisms of ILV formation have been identified, but the relationship between different populations of ILVs and MVBs remains unclear. Here, we show in HeLa cells that different ILV subpopulations can be distinguished by size. EGF stimulation promotes the formation of large ESCRT-dependent ILVs, whereas depletion of the ESCRT-0 component, Hrs, promotes the formation of a uniformly sized population of small ILVs, the formation of which requires CD63. CD63 has previously been implicated in ESCRT-independent sorting of PMEL in MVBs and transfected PMEL is present on the small ILVs that form on Hrs depletion. Upregulation of CD63-dependent ILV formation by Hrs depletion indicates that Hrs and CD63 regulate competing machineries required for the generation of distinct ILV subpopulations. Taken together our results indicate that ILV size is influenced by their cargo and mechanism of formation and suggest a competitive relationship between ESCRT-dependent and -independent mechanisms of ILV formation within single MVBs.
Keywords: CD63; Hrs; cholesterol; intraluminal vesicle; multivesicular endosome.
© 2013 The Authors. Traffic published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The tetraspanin CD63 regulates ESCRT-independent and -dependent endosomal sorting during melanogenesis.Dev Cell. 2011 Oct 18;21(4):708-21. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.019. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Dev Cell. 2011. PMID: 21962903 Free PMC article.
-
Arf GTPase-Activating proteins ADAP1 and ARAP1 regulate incorporation of CD63 in multivesicular bodies.Biol Open. 2024 May 15;13(5):bio060338. doi: 10.1242/bio.060338. Epub 2024 May 10. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 38682696 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for ER:endosome membrane contact sites in ligand-stimulated intraluminal vesicle formation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2018 Oct 19;46(5):1055-1062. doi: 10.1042/BST20170432. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018. PMID: 30242114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between ER-multivesicular body membrane contacts and the ESCRT machinery.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Apr;40(2):464-8. doi: 10.1042/BST20110774. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22435831 Review.
-
Concerted ESCRT and clathrin recruitment waves define the timing and morphology of intraluminal vesicle formation.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 26;9(1):2932. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05345-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30050131 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Membrane Protrusions in Developmental Signaling.J Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 21;10(4):39. doi: 10.3390/jdb10040039. J Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36278544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding extracellular vesicle and nanoparticle heterogeneity: Novel methods and considerations.Proteomics. 2021 Jul;21(13-14):e2000118. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202000118. Epub 2021 May 3. Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33857352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome nanovesicles: biomarkers and new strategies for treatment of human diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jul 15;5(8):e660. doi: 10.1002/mco2.660. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39015555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel TP53 pathway influences the HGS-mediated exosome formation in colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 17;6:28083. doi: 10.1038/srep28083. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27312428 Free PMC article.
-
From Tumor Metastasis towards Cerebral Ischemia-Extracellular Vesicles as a General Concept of Intercellular Communication Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 28;20(23):5995. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235995. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31795140 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Deurs B, Holm PK, Kayser L, Sandvig K. Delivery to lysosomes in the human carcinoma cell line HEp-2 involves an actin filament-facilitated fusion between mature endosomes and preexisting lysosomes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1995;66:309–323. - PubMed
-
- Bright NA, Gratian MJ, Luzio JP. Endocytic delivery to lysosomes mediated by concurrent fusion and kissing events in living cells. Curr Biol. 2005;15:360–365. - PubMed
-
- van Niel G, Porto-Carreiro I, Simoes S, Raposo G. Exosomes: a common pathway for a specialized function. J Biochem. 2006;140:13–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

