Purinergic control of vascular tone in the retina
- PMID: 24277867
- PMCID: PMC3930435
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.267294
Purinergic control of vascular tone in the retina
Abstract
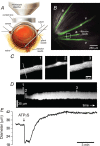
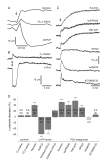
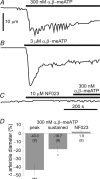
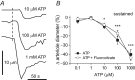
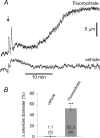
Purinergic control of vascular tone in the CNS has been largely unexplored. This study examines the contribution of endogenous extracellular ATP, acting on vascular smooth muscle cells, in controlling vascular tone in the in vivo rat retina. Retinal vessels were labelled by i.v. injection of a fluorescent dye and imaged with scanning laser confocal microscopy. The diameters of primary arterioles were monitored under control conditions and following intravitreal injection of pharmacological agents. Apyrase (500 units ml(-1)), an ATP hydrolysing enzyme, dilated retinal arterioles by 40.4 ± 2.8%, while AOPCP (12.5 mm), an ecto-5'-nucleotidase inhibitor that increases extracellular ATP levels, constricted arterioles by 58.0 ± 3.8% (P < 0.001 for both), demonstrating the importance of ATP in the control of basal vascular tone. Suramin (500 μm), a broad-spectrum P2 receptor antagonist, dilated retinal arterioles by 50.9 ± 3.7% (P < 0.001). IsoPPADS (300 μm) and TNP-ATP (50 μm), more selective P2X antagonists, dilated arterioles by 41.0 ± 5.3% and 55.2 ± 6.1% respectively (P < 0.001 for both). NF023 (50 μm), a potent antagonist of P2X1 receptors, dilated retinal arterioles by 32.1 ± 2.6% (P < 0.001). A438079 (500 μm) and AZ10606120 (50 μm), P2X7 antagonists, had no effect on basal vascular tone (P = 0.99 and P = 1.00 respectively). In the ex vivo retina, the P2X1 receptor agonist α,β-methylene ATP (300 nm) evoked sustained vasoconstrictions of 18.7 ± 3.2% (P < 0.05). In vivo vitreal injection of the gliotoxin fluorocitrate (150 μm) dilated retinal vessels by 52.3 ± 1.1% (P < 0.001) and inhibited the vasodilatory response to NF023 (50 μm, 7.9 ± 2.0%; P < 0.01). These findings suggest that vascular tone in rat retinal arterioles is maintained by tonic release of ATP from the retina. ATP acts on P2X1 receptors, although contributions from other P2X and P2Y receptors cannot be ruled out. Retinal glial cells are a possible source of the vasoconstricting ATP.
Figures
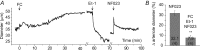
Similar articles
-
Differential effects of uridine adenosine tetraphosphate on purinoceptors in the rat isolated perfused kidney.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;161(3):530-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00914.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20880394 Free PMC article.
-
Dual effects of adenosine on the tone of porcine retinal arterioles in vitro.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Mar 19;55(3):1630-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13428. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24557350
-
Activation of Prejunctional P2x2/3 Heterotrimers by ATP Enhances the Cholinergic Tone in Obstructed Human Urinary Bladders.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020 Jan;372(1):63-72. doi: 10.1124/jpet.119.261610. Epub 2019 Oct 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020. PMID: 31636173
-
Ionotropic purinergic receptor 7 (P2X7) channel structure and pharmacology provides insight regarding non-nucleotide agonism.Channels (Austin). 2024 Dec;18(1):2355150. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2024.2355150. Epub 2024 May 19. Channels (Austin). 2024. PMID: 38762911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and pharmacology of selective P2-purinoceptor antagonists.J Auton Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;16(6):341-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1996.tb00049.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 9131412 Review.
Cited by
-
Astrocytes mediate neurovascular signaling to capillary pericytes but not to arterioles.Nat Neurosci. 2016 Dec;19(12):1619-1627. doi: 10.1038/nn.4428. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27775719 Free PMC article.
-
Physiology of Astroglia.Physiol Rev. 2018 Jan 1;98(1):239-389. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00042.2016. Physiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29351512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cells of the Blood-Brain Barrier: An Overview of the Neurovascular Unit in Health and Disease.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2492:3-24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2289-6_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35733036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocyte contributions to flow/pressure-evoked parenchymal arteriole vasoconstriction.J Neurosci. 2015 May 27;35(21):8245-57. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4486-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26019339 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic regulation of vascular tone in the retrotrapezoid nucleus is specialized to support the drive to breathe.Elife. 2017 Apr 7;6:e25232. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25232. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28387198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akata T. General anaesthetics and vascular smooth muscle: direct actions of general anaesthetics on cellular mechanisms regulating vascular tone. Anesthesiology. 2007;106:365–391. - PubMed
-
- Berkowitz BA, Lukaszew RA, Mullins CM, Penn JS. Impaired hyaloidal circulation function and uncoordinated ocular growth patterns in experimental retinopathy of prematurity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39:391–396. - PubMed
-
- Berstad J. The initial phase of the dextran-induced anaphylactoid reaction in the rat: a comparison of inhibitors of the blood pressure fall. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1982;51:141–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

