IL-17 inhibits chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 24260226
- PMCID: PMC3829852
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079463
IL-17 inhibits chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
Objective: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can differentiate into cells of mesenchymal lineages, such as osteoblasts and chondrocytes. Here we investigated the effects of IL-17, a key cytokine in chronic inflammation, on chondrogenic differentiation of human MSCs.
Methods: Human bone marrow MSCs were pellet cultured in chondrogenic induction medium containing TGF-β3. Chondrogenic differentiation was detected by cartilage matrix accumulation and chondrogenic marker gene expression.
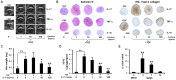
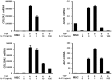
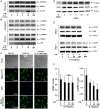
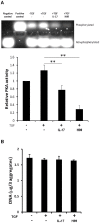
Results: Over-expression of cartilage matrix and chondrogenic marker genes was noted in chondrogenic cultures, but was inhibited by IL-17 in a dose-dependent manner. Expression and phosphorylation of SOX9, the master transcription factor for chondrogenesis, were induced within 2 days and phosphorylated SOX9 was stably maintained until day 21. IL-17 did not alter total SOX9 expression, but significantly suppressed SOX9 phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. At day 7, IL-17 also suppressed the activity of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), which is known to phosphorylate SOX9. H89, a selective PKA inhibitor, also suppressed SOX9 phosphorylation, expression of chondrogenic markers and cartilage matrix, and also decreased chondrogenesis.
Conclusions: IL-17 inhibited chondrogenesis of human MSCs through the suppression of PKA activity and SOX9 phosphorylation. These results suggest that chondrogenic differentiation of MSCs can be inhibited by a mechanism triggered by IL-17 under chronic inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) is required for promoting chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 8;289(32):22048-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.568790. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24962570 Free PMC article.
-
Mangiferin reduces the inhibition of chondrogenic differentiation by IL-1β in mesenchymal stem cells from subchondral bone and targets multiple aspects of the Smad and SOX9 pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Sep 11;15(9):16025-42. doi: 10.3390/ijms150916025. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25216336 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the Interleukin-6/STAT-3 Signaling Pathway to Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 May;67(5):1250-60. doi: 10.1002/art.39036. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25604648
-
The role of Sox9 in collagen hydrogel-mediated chondrogenic differentiation of adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).Biomater Sci. 2018 May 29;6(6):1556-1568. doi: 10.1039/c8bm00317c. Biomater Sci. 2018. Retraction in: Biomater Sci. 2023 Apr 11;11(8):2960. doi: 10.1039/d3bm90028b. PMID: 29696285 Retracted.
-
[The Role of Histone Demethylase in Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Literature Review].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 May;52(3):364-372. doi: 10.12182/20210560202. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 34018352 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
RASL11B gene enhances hyaluronic acid-mediated chondrogenic differentiation in human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells via the activation of Sox9/ERK/smad signals.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 Dec;245(18):1708-1721. doi: 10.1177/1535370220944375. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32878463 Free PMC article.
-
MSC in Tendon and Joint Disease: The Context-Sensitive Link Between Targets and Therapeutic Mechanisms.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 4;10:855095. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.855095. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35445006 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Gut Microbiome Decelerates Fetal Endochondral Bone Formation by Inducing Inflammatory Reaction.Microorganisms. 2022 May 10;10(5):1000. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10051000. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35630443 Free PMC article.
-
Yields and chondrogenic potential of primary synovial mesenchymal stem cells are comparable between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 May 16;8(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0572-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28511664 Free PMC article.
-
A proteomic analysis reveals that Snail regulates the expression of the nuclear orphan receptor Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 2 Group F Member 6 (Nr2f6) and interleukin 17 (IL-17) to inhibit adipocyte differentiation.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015 Feb;14(2):303-15. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.045328. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25505127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alsalameh S, Amin R, Gemba T, Lotz M (2004) Identification of mesenchymal progenitor cells in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum 50: 1522–1532. - PubMed
-
- Dowthwaite GP, Bishop JC, Redman SN, Khan IM, Rooney P, et al. (2004) The surface of articular cartilage contains a progenitor cell population. J Cell Sci 117: 889–897. - PubMed
-
- Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, et al. (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284: 143–147. - PubMed
-
- Sonomoto K, Yamaoka K, Oshita K, Fukuyo S, Zhang X, et al. (2012) Interleukin-1β induces differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts via the Wnt-5a/receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 pathway. Arthritis Rheum 64: 3355–3363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

