CSF p-Tau levels in the prediction of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 24244848
- PMCID: PMC3828758
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.20135447
CSF p-Tau levels in the prediction of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
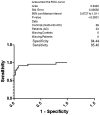
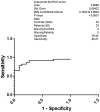
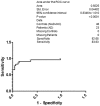
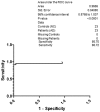
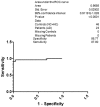
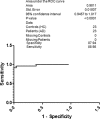
The two hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD) are neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques. Neurofibrillary tangles are formed due to the hyperphosphorylation of tau protein. There is an urgent need to develop a reliable biomarker for the diagnosis of AD. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is surrounding the brain and reflects the major neuropathological features in the AD brain. Diagnosis, disease progression and drug actions rely on the AD biomarkers. Mainly CSF tau and phosphorylated tau (p-Tau) have been observed to serve the purpose for early AD. Keeping in view the early appearance of p-Tau in CSF, we analyzed p-Tau levels in 23 AD, 23 Non AD type dementia (NAD), 23 Neurological control (NC) and 23 Healthy control (HC) North Indian patients. The levels of p-Tau were found to be increased in AD patients (67.87±18.05 pg/ml, SEM 3.76) compared with NAD (47.55±7.85 pg/ml, SEM 1.64), NC (34.42±4.51 pg/ml, SEM 0.94) and HC (27.09±7.18 pg/ml, SEM 1.50). The resulting sensitivity for AD with NAD was 80.27% whereas with respect to the NAD, NC and HC was 85.40%. Therefore elevated levels of p-Tau in AD can be exploited as a predictive biomarker in North Indian AD patients.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; North Indian patients; Sensitivity; p-Tau.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cerebrospinal fluid profile of amyloid β42 (Aβ42), hTau and ubiquitin in North Indian Alzheimer's disease patients.Neurosci Lett. 2011 Jan 7;487(2):134-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.06.075. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Neurosci Lett. 2011. PMID: 20599474
-
Assessment of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) beta-amyloid (1-42), phosphorylated tau (ptau-181) and total Tau protein in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other dementia at Siriraj Hospital, Thailand.J Med Assoc Thai. 2011 Feb;94 Suppl 1:S77-83. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011. PMID: 21721431
-
ApoE4 effects on automated diagnostic classifiers for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Jan 4;4:461-72. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.12.012. eCollection 2014. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 24634832 Free PMC article.
-
CSF biomarkers for amyloid and tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2012 May;47(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9665-5. Epub 2011 Nov 5. J Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22058061 Review.
-
Current Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease: From CSF to Blood.J Pers Med. 2020 Aug 12;10(3):85. doi: 10.3390/jpm10030085. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 32806668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alzheimer's disease and its treatment-yesterday, today, and tomorrow.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 24;15:1399121. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1399121. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38868666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin Resistance is Associated with Higher Cerebrospinal Fluid Tau Levels in Asymptomatic APOEɛ4 Carriers.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;46(2):525-33. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150072. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25812851 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation as a Common Feature of Neurodegenerative Disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 12;10:1008. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01008. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31572186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regularized Linear Discriminant Analysis of EEG Features in Dementia Patients.Front Aging Neurosci. 2016 Nov 30;8:273. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00273. eCollection 2016. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27965568 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Amyloid Beta 1-43 Mirror 1-42 in Relation to Imaging Biomarkers of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2017 Feb 7;9:9. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00009. eCollection 2017. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28223932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buerger K., Zinkowski R., Teipel S. J., Tapiola T., Arai H., Blennow K., Andreasen N., Hofmann-Kiefer K., DeBernardis J., Kerkman D. et al. (2002). Differential diagnosis of Alzheimer disease with cerebrospinal fluid levels of tau protein phosphorylated at threonine 231. Arch. Neurol. 59, 1267–1272 10.1001/archneur.59.8.1267 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

