Crosstalk between NSL histone acetyltransferase and MLL/SET complexes: NSL complex functions in promoting histone H3K4 di-methylation activity by MLL/SET complexes
- PMID: 24244196
- PMCID: PMC3828133
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003940
Crosstalk between NSL histone acetyltransferase and MLL/SET complexes: NSL complex functions in promoting histone H3K4 di-methylation activity by MLL/SET complexes
Abstract
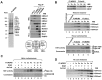
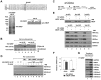
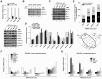
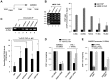
hMOF (MYST1), a histone acetyltransferase (HAT), forms at least two distinct multiprotein complexes in human cells. The male specific lethal (MSL) HAT complex plays a key role in dosage compensation in Drosophila and is responsible for histone H4K16ac in vivo. We and others previously described a second hMOF-containing HAT complex, the non-specific lethal (NSL) HAT complex. The NSL complex has a broader substrate specificity, can acetylate H4 on K16, K5, and K8. The WD (tryptophan-aspartate) repeat domain 5 (WDR5) and host cell factor 1 (HCF1) are shared among members of the MLL/SET (mixed-lineage leukemia/set-domain containing) family of histone H3K4 methyltransferase complexes. The presence of these shared subunits raises the possibility that there are functional links between these complexes and the histone modifications they catalyze; however, the degree to which NSL and MLL/SET influence one another's activities remains unclear. Here, we present evidence from biochemical assays and knockdown/overexpression approaches arguing that the NSL HAT promotes histone H3K4me2 by MLL/SET complexes by an acetylation-dependent mechanism. In genomic experiments, we identified a set of genes including ANKRD2, that are affected by knockdown of both NSL and MLL/SET subunits, suggested they are co-regulated by NSL and MLL/SET complexes. In ChIP assays, we observe that depletion of the NSL subunits hMOF or NSL1 resulted in a significant reduction of both H4K16ac and H3K4me2 in the vicinity of the ANKRD2 transcriptional start site proximal region. However, depletion of RbBP5 (a core component of MLL/SET complexes) only reduced H3K4me2 marks, but not H4K16ac in the same region of ANKRD2, consistent with the idea that NSL acts upstream of MLL/SET to regulate H3K4me2 at certain promoters, suggesting coordination between NSL and MLL/SET complexes is involved in transcriptional regulation of certain genes. Taken together, our results suggest a crosstalk between the NSL and MLL/SET complexes in cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Subunit composition and substrate specificity of a MOF-containing histone acetyltransferase distinct from the male-specific lethal (MSL) complex.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 12;285(7):4268-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C109.087981. Epub 2009 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20018852 Free PMC article.
-
On the mechanism of multiple lysine methylation by the human mixed lineage leukemia protein-1 (MLL1) core complex.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24242-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014498. Epub 2009 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19556245 Free PMC article.
-
The NSL complex regulates housekeeping genes in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(6):e1002736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002736. Epub 2012 Jun 14. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22723752 Free PMC article.
-
MLL1/WDR5 complex in leukemogenesis and epigenetic regulation.Chin J Cancer. 2011 Apr;30(4):240-6. doi: 10.5732/cjc.011.10055. Chin J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21439245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone Acetyltransferase MOF Orchestrates Outcomes at the Crossroad of Oncogenesis, DNA Damage Response, Proliferation, and Stem Cell Development.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Aug 28;40(18):e00232-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00232-20. Print 2020 Aug 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32661120 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone Acetyltransferase Activity of MOF Is Required for MLL-AF9 Leukemogenesis.Cancer Res. 2017 Apr 1;77(7):1753-1762. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2374. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28202522 Free PMC article.
-
Complex-dependent histone acetyltransferase activity of KAT8 determines its role in transcription and cellular homeostasis.Mol Cell. 2021 Apr 15;81(8):1749-1765.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.02.012. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33657400 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of ZFX levels decreases histone H4 acetylation and increases Pol2 pausing at target promoters.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 8;52(12):6850-6865. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae372. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38726870 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of MOF (KAT8) by USP10 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and metastasis through epigenetic activation of ANXA2/Wnt signaling.Oncogene. 2024 Mar;43(12):899-917. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-02955-z. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38317006
-
Capsaicin reactivates hMOF in gastric cancer cells and induces cell growth inhibition.Cancer Biol Ther. 2016 Nov;17(11):1117-1125. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1235654. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Cancer Biol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27715462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin J, Cai Y, Li B, Conaway RC, Workman JL, et al. (2005) In and out: histone variant exchange in chromatin. Trends Biochem Sci 30: 680–687. - PubMed
-
- Berger SL (2007) The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 447: 407–412. - PubMed
-
- Cedar H, Bergman Y (2009) Linking DNA methylation and histone modification: patterns and paradigms. Nat Rev Genet 10: 295–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

