Human cytomegalovirus tegument protein pUL83 inhibits IFI16-mediated DNA sensing for immune evasion
- PMID: 24237704
- PMCID: PMC3876934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.10.007
Human cytomegalovirus tegument protein pUL83 inhibits IFI16-mediated DNA sensing for immune evasion
Abstract
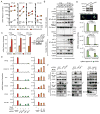
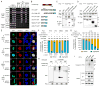
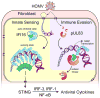
Nuclear sensing of viral DNA has emerged as an essential step in innate immune responses against herpesviruses. Here, we provide mechanistic insight into host recognition of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and subsequent immune evasion by this prominent DNA virus. We establish that the interferon-inducible protein IFI16 acts as a nuclear DNA sensor following HCMV infection, binding viral DNA and triggering expression of antiviral cytokines via the STING-TBK1-IRF3 signaling pathway. The HCMV tegument protein pUL83 inhibits this response by interacting with the IFI16 pyrin domain, blocking its oligomerization upon DNA sensing and subsequent immune signals. pUL83 disrupts IFI16 by concerted action of its N- and C-terminal domains, in which an evolutionarily conserved N-terminal pyrin association domain (PAD) binds IFI16. Additionally, phosphorylation of the N-terminal domain modulates pUL83-mediated inhibition of pyrin aggregation. Collectively, our data elucidate the interplay between host DNA sensing and HCMV immune evasion, providing targets for restoring antiviral immunity.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulatory Interaction between the Cellular Restriction Factor IFI16 and Viral pp65 (pUL83) Modulates Viral Gene Expression and IFI16 Protein Stability.J Virol. 2016 Aug 26;90(18):8238-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00923-16. Print 2016 Sep 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27384655 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Tegument Protein pp65 (pUL83) Dampens Type I Interferon Production by Inactivating the DNA Sensor cGAS without Affecting STING.J Virol. 2018 Feb 26;92(6):e01774-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01774-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29263269 Free PMC article.
-
Viral DNA Sensors IFI16 and Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase Possess Distinct Functions in Regulating Viral Gene Expression, Immune Defenses, and Apoptotic Responses during Herpesvirus Infection.mBio. 2016 Nov 15;7(6):e01553-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01553-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27935834 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus tegument protein pp65 (pUL83): a key player in innate immune evasion.New Microbiol. 2018 Apr;41(2):87-94. Epub 2018 Jan 31. New Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29384558 Review.
-
The tiers and dimensions of evasion of the type I interferon response by human cytomegalovirus.J Mol Biol. 2013 Dec 13;425(24):4857-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.08.023. Epub 2013 Sep 5. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24013068 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
cGAS-STING Signaling Regulates Initial Innate Control of Cytomegalovirus Infection.J Virol. 2016 Aug 12;90(17):7789-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01040-16. Print 2016 Sep 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27334590 Free PMC article.
-
The functional interactome of PYHIN immune regulators reveals IFIX is a sensor of viral DNA.Mol Syst Biol. 2015 Feb 9;11(1):787. doi: 10.15252/msb.20145808. Mol Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 25665578 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Interaction between the Cellular Restriction Factor IFI16 and Viral pp65 (pUL83) Modulates Viral Gene Expression and IFI16 Protein Stability.J Virol. 2016 Aug 26;90(18):8238-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00923-16. Print 2016 Sep 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27384655 Free PMC article.
-
Early Nuclear Events after Herpesviral Infection.J Clin Med. 2019 Sep 7;8(9):1408. doi: 10.3390/jcm8091408. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31500286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytosolic Recognition of Microbes and Pathogens: Inflammasomes in Action.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018 Sep 12;82(4):e00015-18. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00015-18. Print 2018 Dec. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30209070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnon TI, Achdout H, Levi O, Markel G, Saleh N, Katz G, Gazit R, Gonen-Gross T, Hanna J, Nahari E, et al. Inhibition of the NKp30 activating receptor by pp65 of human cytomegalovirus. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:515–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

