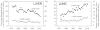Changing rates for liver and lung cancers in Qidong, China
- PMID: 24215631
- PMCID: PMC3946948
- DOI: 10.1021/tx400313j
Changing rates for liver and lung cancers in Qidong, China
Abstract
Residents of Qidong, China are undergoing a rapid fluctuation in cancer incidence rates at many organ sites, reflecting a dynamic interplay of socio-behavioral, economic, and environmental factors. This Perspective On Statistical Trends examines the China age-standardized incidence rates (CASR), as tracked by the Qidong Cancer Registry for the past 40 years, for the two leading cancer killers in Qidong, liver and lung. Both cancer types are strongly influenced by environmental factors. The CASR for liver cancer has dropped nearly 50% in the last 4 decades, in part from access to deep-well drinking water in the 1970s with consequent diminished exposure to tumor promoting microcystins produced by blue-green algae. There have also been substantive reductions in exposures to dietary aflatoxins, as economic reform in the mid-1980s fostered a wholesale change in dietary staple from maize to rice. In men, lung cancer CASR has trebled over this period, likely driven by a high prevalence of smokers (∼65%) and an ever increasing smoking frequency in this population. Qidong women, by contrast, rarely smoke and have exhibited a flat CASR until the past decade where lung cancer rates have now doubled. This upturn may reflect an increasing burden of indoor and outdoor air pollution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Qidong: a crucible for studies on liver cancer etiology and prevention.Cancer Biol Med. 2019 Feb;16(1):24-37. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2018.0394. Cancer Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31119044 Free PMC article.
-
[Trends in the mortality of liver cancer in Qidong, China: an analysis of fifty years].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2012 Jul;34(7):532-7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2012.07.012. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22967473 Chinese.
-
Lung Cancer in a Rural Area of China: Rapid Rise in Incidence and Poor Improvement in Survival.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(16):7295-302. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.16.7295. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 26514527
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diet as a confounder of the association between air pollution and female lung cancer: Hong Kong studies on exposures to environmental tobacco smoke, incense, and cooking fumes as examples.Lung Cancer. 1996 Mar;14 Suppl 1:S47-61. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5002(96)90210-x. Lung Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8785667 Review.
Cited by
-
The Challenges of Designing and Implementing Clinical Trials With Broccoli Sprouts… and Turning Evidence Into Public Health Action.Front Nutr. 2021 Apr 29;8:648788. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.648788. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33996874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver cancer mortality over six decades in an epidemic area: what we have learned.PeerJ. 2021 Feb 3;9:e10600. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10600. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33604165 Free PMC article.
-
miR-149 in Human Cancer: A Systemic Review.J Cancer. 2018 Jan 1;9(2):375-388. doi: 10.7150/jca.21044. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29344284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer survival in Qidong between 1972 and 2011: A population-based analysis.Mol Clin Oncol. 2017 Jun;6(6):944-954. doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1234. Epub 2017 May 3. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28588795 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of MicroRNA Expression Profiling Involved in MC-LR-Induced Cytotoxicity by High-Throughput Sequencing.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Jan 7;9(1):23. doi: 10.3390/toxins9010023. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28067858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen JG, Zhu J, Zhang YH, Lu JH. Cancer survival in Qidong, China, 1992–2000. IARC Sci Publ. 2011;162:43–53. - PubMed
-
- Chen JG, editor. Cancer in Qidong, China (1972–2011) Beijing: Military Medical Scientific Press; 2013. pp. 1–346.
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Kensler TW, Qian GS, Chen JG, Groopman JD. Translational strategies for cancer prevention in liver. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:321–329. - PubMed
-
- Ming L, Thorgeirsson SS, Gail MH, Lu P, Harris CC, Wang N, Shao Y, Wu Z, Liu G, Wang X, Sun Z. Dominant role of hepatitis B virus and cofactor role of aflatoxin in hepatocarcinogenesis in Qidong, China. Hepatology. 2002;36:1214–1220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous