Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012
- PMID: 24206586
- PMCID: PMC3837670
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1911.130792
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012
Abstract
We report a retrospectively identified fatal case of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) in South Korea from 2012. SFTS virus was isolated from the stored blood of the patient. Phylogenetic analysis revealed this isolate was closely related to SFTS virus strains from China and Japan.
Keywords: South Korea; bunyavirus; phlebovirus; severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome; viruses.
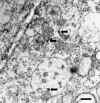
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phylogenetic and Geographic Relationships of Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus in China, South Korea, and Japan.J Infect Dis. 2015 Sep 15;212(6):889-98. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv144. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25762790
-
Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection, South Korea, 2010.Emerg Infect Dis. 2018 Nov;24(11):2103-2105. doi: 10.3201/eid2411.170756. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30334706 Free PMC article.
-
Endemic Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Vietnam.Emerg Infect Dis. 2019 May;25(5):1029-1031. doi: 10.3201/eid2505.181463. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31002059 Free PMC article.
-
[Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and development of specific treatment and prevention measures].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2018;59(10):2255-2259. doi: 10.11406/rinketsu.59.2255. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2018. PMID: 30305533 Review. Japanese.
-
Pathophysiology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and development of specific antiviral therapy.J Infect Chemother. 2018 Oct;24(10):773-781. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Aug 8. J Infect Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30098914 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic and pathogenic diversity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) in South Korea.JCI Insight. 2020 Jan 30;5(2):e129531. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.129531. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 31877113 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Tick-Borne Diseases.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020 Jan 2;33(2):e00083-18. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00083-18. Print 2020 Mar 18. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 31896541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Four Year Surveillance of the Vector Hard Ticks for SFTS, Ganghwa-do, Republic of Korea.Korean J Parasitol. 2019 Dec;57(6):691-698. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2019.57.6.691. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Korean J Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31914523 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features and epidemiology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in dogs in the Republic of Korea: an observational study (2019-2020).Vet Res Commun. 2022 Dec;46(4):1195-1207. doi: 10.1007/s11259-022-09979-4. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Vet Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35932407 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Viral Coinfection of the Ixodes persulcatus Ticks Feeding on Humans in a Natural Focus of the South of the Far East.Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 12;11(7):1791. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071791. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang YZ, Zhou DJ, Xiong Y, Chen XP, He YW, Sun Q, et al. Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel tick-borne Bunyavirus in Huaiyangshan, China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2011;32:209–20 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
