Stable pausing by RNA polymerase II provides an opportunity to target and integrate regulatory signals
- PMID: 24184211
- PMCID: PMC3845087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.10.001
Stable pausing by RNA polymerase II provides an opportunity to target and integrate regulatory signals
Abstract
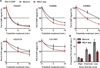
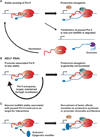
Metazoan gene expression is often regulated after the recruitment of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) to promoters, through the controlled release of promoter-proximally paused Pol II into productive RNA synthesis. Despite the prevalence of paused Pol II, very little is known about the dynamics of these early elongation complexes or the fate of the short transcription start site-associated (tss) RNAs they produce. Here, we demonstrate that paused elongation complexes can be remarkably stable, with half-lives exceeding 15 min at genes with inefficient pause release. Promoter-proximal termination by Pol II is infrequent, and released tssRNAs are targeted for rapid degradation. Further, we provide evidence that the predominant tssRNA species observed are nascent RNAs held within early elongation complexes. We propose that stable pausing of polymerase provides a temporal window of opportunity for recruitment of factors to modulate gene expression and that the nascent tssRNA represents an appealing target for these interactions.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Integrator Complex Attenuates Promoter-Proximal Transcription at Protein-Coding Genes.Mol Cell. 2019 Dec 5;76(5):738-752.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.10.034. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31809743 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of promoter Pol II on Hsp70 reveal stable pausing and key insights into its regulation.Genes Dev. 2014 Jan 1;28(1):14-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.231886.113. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24395245 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of histone H3 at Ser10 facilitates RNA polymerase II release from promoter-proximal pausing in Drosophila.Genes Dev. 2007 Nov 1;21(21):2818-31. doi: 10.1101/gad.1604007. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17942706 Free PMC article.
-
Getting up to speed with transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Mar;16(3):167-77. doi: 10.1038/nrm3953. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25693130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II: a nexus of gene regulation.Genes Dev. 2019 Aug 1;33(15-16):960-982. doi: 10.1101/gad.325142.119. Epub 2019 May 23. Genes Dev. 2019. PMID: 31123063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Exosome Regulates AID DNA Mutator Activity in the B Cell Genome.Adv Immunol. 2015;127:257-308. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 May 14. Adv Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26073986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional speed bumps revealed in high resolution.Nature. 2018 Aug;560(7720):560-561. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-05971-8. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30143755 No abstract available.
-
Reporter-ChIP-nexus reveals strong contribution of the Drosophila initiator sequence to RNA polymerase pausing.Elife. 2019 Apr 25;8:e41461. doi: 10.7554/eLife.41461. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31021316 Free PMC article.
-
A combinatorial view of old and new RNA polymerase II modifications.Transcription. 2020 Apr;11(2):66-82. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2020.1762468. Epub 2020 May 13. Transcription. 2020. PMID: 32401151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative DNA secondary structure formation affects RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing in human.Genome Biol. 2018 Jul 12;19(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1463-8. Genome Biol. 2018. PMID: 30001206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barboric M, Nissen RM, Kanazawa S, Jabrane-Ferrat N, Peterlin BM. NF-kappaB binds P-TEFb to stimulate transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell. 2001;8:327–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

