Oncogenic and drug-sensitive NTRK1 rearrangements in lung cancer
- PMID: 24162815
- PMCID: PMC3823836
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3352
Oncogenic and drug-sensitive NTRK1 rearrangements in lung cancer
Abstract
We identified new gene fusions in patients with lung cancer harboring the kinase domain of the NTRK1 gene that encodes the high-affinity nerve growth factor receptor (TRKA protein). Both the MPRIP-NTRK1 and CD74-NTRK1 fusions lead to constitutive TRKA kinase activity and are oncogenic. Treatment of cells expressing NTRK1 fusions with inhibitors of TRKA kinase activity inhibited autophosphorylation of TRKA and cell growth. Tumor samples from 3 of 91 patients with lung cancer (3.3%) without known oncogenic alterations assayed by next-generation sequencing or fluorescence in situ hybridization demonstrated evidence of NTRK1 gene fusions.
Figures
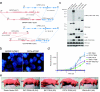
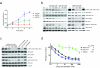
Comment in
-
Lung cancer: drug-sensitivity--time for a rearrangement?Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013 Dec;10(12):670. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.216. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24217201 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Identification of Existing Drugs That Effectively Target NTRK1 and ROS1 Rearrangements in Lung Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 1;23(1):204-213. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1601. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27370605 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of NTRK1 Fusion as Resistance Mechanism to EGFR TKI in EGFR+ NSCLC: Results From a Large-Scale Survey of NTRK1 Fusions in Chinese Patients With Lung Cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2020 May;21(3):247-254. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2019.09.004. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Clin Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31761448
-
Chromosomal rearrangements involving the NTRK1 gene in colorectal carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2015 Aug 28;365(1):107-11. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.05.013. Epub 2015 May 19. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 26001971
-
Oncogenic rearrangements of the NTRK1/NGF receptor.Cancer Lett. 2006 Jan 28;232(1):90-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.07.043. Epub 2005 Oct 20. Cancer Lett. 2006. PMID: 16242838 Review.
-
Detecting and Targeting NTRK Fusions in Cancer in the Era of Tumor Agnostic Oncology.Drugs. 2021 Mar;81(4):445-452. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01459-w. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33400240 Review.
Cited by
-
(R)-2-Phenylpyrrolidine Substituted Imidazopyridazines: A New Class of Potent and Selective Pan-TRK Inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015 Mar 16;6(5):562-7. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00050. eCollection 2015 May 14. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 26005534 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Therapies in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-Beyond EGFR and ALK.Cancers (Basel). 2015 May 26;7(2):930-49. doi: 10.3390/cancers7020816. Cancers (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26018876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secretory carcinoma around Stensen's duct misdiagnosed as salivary duct cyst.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 Aug 1;13(8):2211-2217. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32922622 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of CD74 Occurrence in Oncogenic Fusion Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 5;24(21):15981. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115981. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor evolution in epidermal growth factor receptor mutated non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2020 May;12(5):2896-2909. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.08.31. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32642202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mok TS, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, et al. Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013 - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi K, et al. RET, ROS1 and ALK fusions in lung cancer. Nat Med. 2012;18:378–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

