ATHENA: the analysis tool for heritable and environmental network associations
- PMID: 24149050
- PMCID: PMC3933870
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt572
ATHENA: the analysis tool for heritable and environmental network associations
Abstract
Motivation: Advancements in high-throughput technology have allowed researchers to examine the genetic etiology of complex human traits in a robust fashion. Although genome-wide association studies have identified many novel variants associated with hundreds of traits, a large proportion of the estimated trait heritability remains unexplained. One hypothesis is that the commonly used statistical techniques and study designs are not robust to the complex etiology that may underlie these human traits. This etiology could include non-linear gene × gene or gene × environment interactions. Additionally, other levels of biological regulation may play a large role in trait variability.
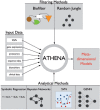
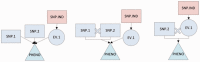
Results: To address the need for computational tools that can explore enormous datasets to detect complex susceptibility models, we have developed a software package called the Analysis Tool for Heritable and Environmental Network Associations (ATHENA). ATHENA combines various variable filtering methods with machine learning techniques to analyze high-throughput categorical (i.e. single nucleotide polymorphisms) and quantitative (i.e. gene expression levels) predictor variables to generate multivariable models that predict either a categorical (i.e. disease status) or quantitative (i.e. cholesterol levels) outcomes. The goal of this article is to demonstrate the utility of ATHENA using simulated and biological datasets that consist of both single nucleotide polymorphisms and gene expression variables to identify complex prediction models. Importantly, this method is flexible and can be expanded to include other types of high-throughput data (i.e. RNA-seq data and biomarker measurements).
Availability: ATHENA is freely available for download. The software, user manual and tutorial can be downloaded from http://ritchielab.psu.edu/ritchielab/software.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATHENA: a tool for meta-dimensional analysis applied to genotypes and gene expression data to predict HDL cholesterol levels.Pac Symp Biocomput. 2013:385-96. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2013. PMID: 23424143 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol for Construction of Genome-Wide Epistatic SNP Networks Using WISH-R Package.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2212:155-168. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0947-7_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33733355
-
A multivariate regression approach to association analysis of a quantitative trait network.Bioinformatics. 2009 Jun 15;25(12):i204-12. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp218. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19477989 Free PMC article.
-
What is the natural measurement unit of temperament: single traits or profiles?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Apr 19;373(1744):20170163. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0163. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29483348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multigenic modeling of complex disease by random forests.Adv Genet. 2010;72:73-99. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380862-2.00004-7. Adv Genet. 2010. PMID: 21029849 Review.
Cited by
-
Personalized Medicine Approach to Proteomics and Metabolomics of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes: A Narrative Review.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2024 Sep 13. doi: 10.1007/s13318-024-00912-5. Online ahead of print. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2024. PMID: 39269556 Review.
-
A practical introduction to holo-omics.Cell Rep Methods. 2024 Jul 15;4(7):100820. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100820. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Cell Rep Methods. 2024. PMID: 38986611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Role of Multi-Omics Approaches in the Study of Retinal Vascular Diseases.Cells. 2022 Dec 26;12(1):103. doi: 10.3390/cells12010103. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What makes a good prediction? Feature importance and beginning to open the black box of machine learning in genetics.Hum Genet. 2022 Sep;141(9):1515-1528. doi: 10.1007/s00439-021-02402-z. Epub 2021 Dec 4. Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 34862561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel EDGE encoding method enhances ability to identify genetic interactions.PLoS Genet. 2021 Jun 4;17(6):e1009534. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009534. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34086673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aulchenko YS, et al. GenABEL: an R library for genome-wide association analysis. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:1294–1296. - PubMed
-
- Bishop CM. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition. London: Oxford University Press; 1995.
-
- Breiman L. Random Forests. Machine Learning. 2001;45:5–32.
-
- Carniak E. Bayesian networks without tears. AI Magazine. 1991:50–63.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

