Understanding the impact of 2D and 3D fibroblast cultures on in vitro breast cancer models
- PMID: 24124550
- PMCID: PMC3790689
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076373
Understanding the impact of 2D and 3D fibroblast cultures on in vitro breast cancer models
Abstract
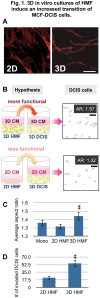
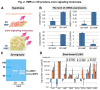
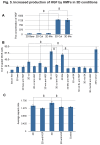
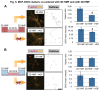
The utilization of 3D, physiologically relevant in vitro cancer models to investigate complex interactions between tumor and stroma has been increasing. Prior work has generally focused on the cancer cells and, the role of fibroblast culture conditions on tumor-stromal cell interactions is still largely unknown. Here, we focus on the stroma by comparing functional behaviors of human mammary fibroblasts (HMFs) cultured in 2D and 3D and their effects on the invasive progression of breast cancer cells (MCF10DCIS.com). We identified increased levels of several paracrine factors from HMFs cultured in 3D conditions that drive the invasive transition. Using a microscale co-culture model with improved compartmentalization and sensitivity, we demonstrated that HMFs cultured in 3D intensify the promotion of the invasive progression through the HGF/c-Met interaction. This study highlights the importance of the 3D stromal microenvironment in the development of multiple cell type in vitro cancer models.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of HGF in epithelial-stromal cell interactions during progression from benign breast disease to ductal carcinoma in situ.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(5):R82. doi: 10.1186/bcr3476. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24025166 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast hepatocyte growth factor promotes invasion of human mammary ductal carcinoma in situ.Cancer Res. 2009 Dec 1;69(23):9148-55. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1043. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19920187 Free PMC article.
-
A Human Organotypic Microfluidic Tumor Model Permits Investigation of the Interplay between Patient-Derived Fibroblasts and Breast Cancer Cells.Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 15;79(12):3139-3151. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2293. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30992322 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-stromal interactions in breast tumor progression--significance of histological heterogeneity of tumor-stromal fibroblasts.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013 Apr;17(4):449-60. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.757305. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013. PMID: 23297753 Review.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor and the Met system as a mediator of tumor-stromal interactions.Int J Cancer. 2006 Aug 1;119(3):477-83. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21808. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16453287 Review.
Cited by
-
The SUMO protease SENP1 promotes aggressive behaviors of high HIF2α expressing renal cell carcinoma cells.Oncogenesis. 2022 Oct 25;11(1):65. doi: 10.1038/s41389-022-00440-4. Oncogenesis. 2022. PMID: 36284084 Free PMC article.
-
Crotoxin Modulates Events Involved in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in 3D Spheroid Model.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Nov 22;13(11):830. doi: 10.3390/toxins13110830. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34822613 Free PMC article.
-
Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Dec 16;6(1):426. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00830-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34916490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluid shear stress stimulates breast cancer cells to display invasive and chemoresistant phenotypes while upregulating PLAU in a 3D bioreactor.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2019 Nov;116(11):3084-3097. doi: 10.1002/bit.27119. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2019. PMID: 31317530 Free PMC article.
-
Studying Adipose Tissue in the Breast Tumor Microenvironment In Vitro: Progress and Opportunities.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020 Dec;17(6):773-785. doi: 10.1007/s13770-020-00299-9. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020. PMID: 32939672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

