Characterization of CD44 variant expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
- PMID: 24122205
- PMCID: PMC3967078
- DOI: 10.1007/s13277-013-1272-3
Characterization of CD44 variant expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
Abstract
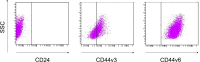
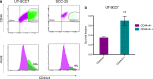
CD44 is a complex family of molecules, associated with aggressive malignancies and cancer stem cells. However, the role of CD44 variants in tumor progression and treatment resistance is not clear. In this study, the expression of CD44 and its variants was assessed in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC). Furthermore, subpopulations of cells expressing high amounts of CD44 variants were identified and characterized, for e.g., cell cycle phase and radioresistance. Results revealed high and homogenous CD44 and CD44v7 expression in four cell lines and CD44v4 and CD44v6 in three cell lines. CD44v3 was highly expressed in two cell lines, whereas CD44v5, CD44v7/8, CD44v10, CD133, and CD24 demonstrated no or moderate expression. Moreover, a subpopulation of very high CD44v4 expression was identified, which is independent of cell phase, demonstrating increased proliferation and radioresistance. In cell starvation experiments designed to enrich for cancer stem cells, a large population with dramatically increased expression of CD44, CD44v3, CD44v6, and CD44v7 was formed. Expression was independent of cell phase, and cells demonstrated increased radioresistance and migration rate. Our results demonstrate that the heterogeneity of tumor cells has important clinical implications for the treatment of HNSCC and that some of the CD44 variants may be associated with increased radioresistance. Highly expressed CD44 variants could make interesting candidates for selective cancer targeting.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of CD44 variant expression in oral, head and neck squamous cell carcinomas using a triple approach and its clinical significance.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2014 Jul-Sep;27(3):337-49. doi: 10.1177/039463201402700304. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25280025 Free PMC article.
-
CD44 variant isoforms in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression.Laryngoscope. 2009 Aug;119(8):1518-30. doi: 10.1002/lary.20506. Laryngoscope. 2009. PMID: 19507218 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between Raf-MEK-ERK and PI3K-Akt-GSK3β signaling networks promotes chemoresistance, invasion/migration and stemness via expression of CD44 variants (v4 and v6) in oral cancer.Oral Oncol. 2018 Nov;86:234-243. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.09.028. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Oral Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30409306
-
Activation of Matrix Hyaluronan-Mediated CD44 Signaling, Epigenetic Regulation and Chemoresistance in Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Aug 24;18(9):1849. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091849. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28837080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of hyaluronan-mediated CD44 signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression and chemoresistance.Am J Pathol. 2011 Mar;178(3):956-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.11.077. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21356346 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cargo and Functional Profile of Saliva-Derived Exosomes Reveal Biomarkers Specific for Head and Neck Cancer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 11;9:904295. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.904295. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35899209 Free PMC article.
-
CD44v6-Targeted Imaging of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Antibody-Based Approaches.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2017 Jun 20;2017:2709547. doi: 10.1155/2017/2709547. eCollection 2017. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2017. PMID: 29097914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD44v3 protein-carrying tumor-derived exosomes in HNSCC patients' plasma as potential noninvasive biomarkers of disease activity.Oncoimmunology. 2020 Apr 7;9(1):1747732. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1747732. eCollection 2020. Oncoimmunology. 2020. PMID: 32313730 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of CD44v6 may lead to recurrent spontaneous abortion by inhibiting the proliferation and migration of trophoblast cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Apr 1;11(4):2072-2079. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31938314 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of exosomes in radiotherapy.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Oct 31;20(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00986-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36316715 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

