Partially penetrant postnatal lethality of an epithelial specific MicroRNA in a mouse knockout
- PMID: 24116130
- PMCID: PMC3792019
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076634
Partially penetrant postnatal lethality of an epithelial specific MicroRNA in a mouse knockout
Abstract
MicroRNAs are small noncoding RNAs thought to have pivotal roles in numerous diseases and developmental processes. However, a growing body of literature indicates that in vivo elimination of these tiny RNAs usually has little to no observable consequence, suggesting functional redundancy with other microRNAs or cellular pathways. We provide an in-depth analysis of miR-205 expression and define miR-205 as an epithelial-specific microRNA, and for the first time show that ablation of this microRNA knockout exhibits partially penetrant lethality in a constitutive mouse knockout model. Given the role of this microRNA in cancer and development, this mouse model will be an incredible reagent to study the function and mechanisms of miR-205 in epithelial tissue development and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
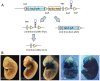
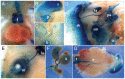
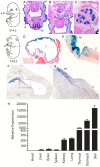
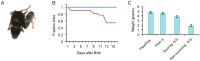
Similar articles
-
Mir-290-295 deficiency in mice results in partially penetrant embryonic lethality and germ cell defects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 23;108(34):14163-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111241108. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21844366 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-127 Promotes Mesendoderm Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells by Targeting Left-Right Determination Factor 2.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 3;291(23):12126-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.723247. Epub 2016 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27072135 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-429 functions as a regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting Pcdh8 during murine embryo implantation.Hum Reprod. 2015 Mar;30(3):507-18. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev001. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Hum Reprod. 2015. PMID: 25609238
-
Mutation of murine Sox4 untranslated regions results in partially penetrant perinatal lethality.In Vivo. 2014 Sep-Oct;28(5):709-18. In Vivo. 2014. PMID: 25189881 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput discovery of novel developmental phenotypes.Nature. 2016 Sep 22;537(7621):508-514. doi: 10.1038/nature19356. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27626380 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: New approaches for better diagnosis and therapy.Transl Oncol. 2021 Jul;14(7):101090. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101090. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33831655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-205 Maintains T Cell Development following Stress by Regulating Forkhead Box N1 and Selected Chemokines.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 28;291(44):23237-23247. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.744508. Epub 2016 Sep 19. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27646003 Free PMC article.
-
Metazoan MicroRNAs.Cell. 2018 Mar 22;173(1):20-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.006. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29570994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the ups and downs of miR-205 in physiology and cancer: transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Nov 15;11(11):980. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03192-4. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33191398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of MiR-205 As a MicroRNA That Is Highly Expressed in Medullary Thymic Epithelial Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 13;10(8):e0135440. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135440. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26270036 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

