Reactive oxygen species are required for 5-HT-induced transactivation of neuronal platelet-derived growth factor and TrkB receptors, but not for ERK1/2 activation
- PMID: 24086766
- PMCID: PMC3785432
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077027
Reactive oxygen species are required for 5-HT-induced transactivation of neuronal platelet-derived growth factor and TrkB receptors, but not for ERK1/2 activation
Abstract
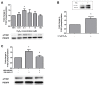
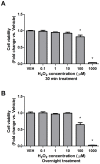
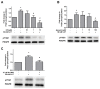
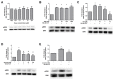
High concentrations of reactive oxygen species (ROS) induce cellular damage, however at lower concentrations ROS act as intracellular second messengers. In this study, we demonstrate that serotonin (5-HT) transactivates the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) type β receptor as well as the TrkB receptor in neuronal cultures and SH-SY5Y cells, and that the transactivation of both receptors is ROS-dependent. Exogenous application of H₂O₂ induced the phosphorylation of these receptors in a dose-dependent fashion, similar to that observed with 5-HT. However the same concentrations of H₂O₂ failed to increase ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Yet, the NADPH oxidase inhibitors diphenyleneiodonium chloride and apocynin blocked both 5-HT-induced PDGFβ receptor phosphorylation and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. The increases in PDGFβ receptor and ERK1/2 phosphorylation were also dependent on protein kinase C activity, likely acting upstream of NADPH oxidase. Additionally, although the ROS scavenger N-acetyl-l-cysteine abrogated 5-HT-induced PDGFβ and TrkB receptor transactivation, it was unable to prevent 5-HT-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Thus, the divergence point for 5-HT-induced receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) transactivation and ERK1/2 phosphorylation occurs at the level of NADPH oxidase in this system. The ability of 5-HT to induce the production of ROS resulting in transactivation of both PDGFβ and TrkB receptors may suggest that instead of a single GPCR to single RTK pathway, a less selective, more global RTK response to GPCR activation is occurring.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
5-HT(1A) receptors transactivate the platelet-derived growth factor receptor type beta in neuronal cells.Cell Signal. 2013 Jan;25(1):133-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.09.021. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23006663
-
Fluoxetine-induced transactivation of the platelet-derived growth factor type β receptor reveals a novel heterologous desensitization process.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015 Mar;65:45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.02.013. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25702926
-
Non-transactivational, dual pathways for LPA-induced Erk1/2 activation in primary cultures of brown pre-adipocytes.Exp Cell Res. 2010 Oct 1;316(16):2664-75. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.05.029. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Exp Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 20576526
-
NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of ERK1/2 is required for apoptosis of human neutrophils induced by Entamoeba histolytica.J Immunol. 2005 Apr 1;174(7):4279-88. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.7.4279. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15778391
-
GPCR transactivation signalling in vascular smooth muscle cells: role of NADPH oxidases and reactive oxygen species.Vasc Biol. 2019 Jul 23;1(1):R1-R11. doi: 10.1530/VB-18-0004. eCollection 2019. Vasc Biol. 2019. PMID: 32923966 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ROS and ROS-Mediated Cellular Signaling.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:4350965. doi: 10.1155/2016/4350965. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 26998193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin Heteroreceptor Complexes and Their Integration of Signals in Neurons and Astroglia-Relevance for Mental Diseases.Cells. 2021 Jul 27;10(8):1902. doi: 10.3390/cells10081902. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal Molecular Hydrogen Administration Ameliorates Several Findings in Nitrofen-Induced Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 31;22(17):9500. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179500. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502408 Free PMC article.
-
The hallucinogen 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine hydrochloride activates neurotrophin receptors in a neuronal cell line and promotes neurites extension.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2017 Jun;124(6):749-759. doi: 10.1007/s00702-017-1706-y. Epub 2017 Mar 18. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2017. PMID: 28315978
-
5-HT7 receptor activation promotes an increase in TrkB receptor expression and phosphorylation.Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 Nov 7;8:391. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00391. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25426041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steiner JA, Carneiro AM, Blakely RD (2008) Going with the flow: trafficking-dependent and -independent regulation of serotonin transport. Traffic 9: 1393-1402. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00757.x. PubMed: 18445122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Monti JM, Jantos H (2008) The roles of dopamine and serotonin, and of their receptors, in regulating sleep and waking. Prog Brain Res 172: 625-646. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00929-1. PubMed: 18772053. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Geldenhuys WJ, Van der Schyf CJ (2009) The serotonin 5-HT6 receptor: a viable drug target for treating cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother 9: 1073-1085. doi:10.1586/ern.09.51. PubMed: 19589055. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alex KD, Pehek EA (2007) Pharmacologic mechanisms of serotonergic regulation of dopamine neurotransmission. Pharmacol Ther 113: 296-320. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.08.004. PubMed: 17049611. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

