Rasputin functions as a positive regulator of orb in Drosophila oogenesis
- PMID: 24069162
- PMCID: PMC3771913
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072864
Rasputin functions as a positive regulator of orb in Drosophila oogenesis
Abstract
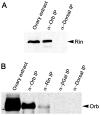
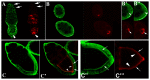
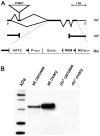
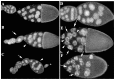
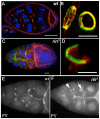
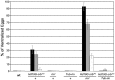
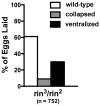
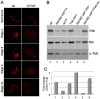
The determination of cell fate and the establishment of polarity axes during Drosophila oogenesis depend upon pathways that localize mRNAs within the egg chamber and control their on-site translation. One factor that plays a central role in regulating on-site translation of mRNAs is Orb. Orb is a founding member of the conserved CPEB family of RNA-binding proteins. These proteins bind to target sequences in 3' UTRs and regulate mRNA translation by modulating poly(A) tail length. In addition to controlling the translation of axis-determining mRNAs like grk, fs(1)K10, and osk, Orb protein autoregulates its own synthesis by binding to orb mRNA and activating its translation. We have previously shown that Rasputin (Rin), the Drosophila homologue of Ras-GAP SH3 Binding Protein (G3BP), associates with Orb in a messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) complex. Rin is an evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding protein believed to function as a link between Ras signaling and RNA metabolism. Here we show that Orb and Rin form a complex in the female germline. Characterization of a new rin allele shows that rin is essential for oogenesis. Co-localization studies suggest that Orb and Rin form a complex in the oocyte at different stages of oogenesis. This is supported by genetic and biochemical analyses showing that rin functions as a positive regulator in the orb autoregulatory pathway by increasing Orb protein expression. Tandem Mass Spectrometry analysis shows that several canonical stress granule proteins are associated with the Orb-Rin complex suggesting that a conserved mRNP complex regulates localized translation during oogenesis in Drosophila.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Drosophila fragile X protein functions as a negative regulator in the orb autoregulatory pathway.Dev Cell. 2005 Mar;8(3):331-42. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.011. Dev Cell. 2005. PMID: 15737929
-
Functioning of the Drosophila orb gene in gurken mRNA localization and translation.Development. 2001 Aug;128(16):3169-77. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.16.3169. Development. 2001. PMID: 11688565
-
The CPEB translational regulator, Orb, functions together with Par proteins to polarize the Drosophila oocyte.PLoS Genet. 2019 Mar 13;15(3):e1008012. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008012. eCollection 2019 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 30865627 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetics of the early stages of germ cell differentiation during Drosophila oogenesis.Ciba Found Symp. 1994;182:210-9; discussion 219-22. doi: 10.1002/9780470514573.ch12. Ciba Found Symp. 1994. PMID: 7835152 Review.
-
Localization, anchoring and translational control of oskar, gurken, bicoid and nanos mRNA during Drosophila oogenesis.Fly (Austin). 2009 Jan-Mar;3(1):15-28. doi: 10.4161/fly.3.1.7751. Epub 2009 Jan 2. Fly (Austin). 2009. PMID: 19182536 Review.
Cited by
-
Alphavirus Infection: Host Cell Shut-Off and Inhibition of Antiviral Responses.Viruses. 2016 Jun 11;8(6):166. doi: 10.3390/v8060166. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27294951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A single-cell atlas and lineage analysis of the adult Drosophila ovary.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 6;11(1):5628. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19361-0. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33159074 Free PMC article.
-
Mosquito Rasputin interacts with chikungunya virus nsP3 and determines the infection rate in Aedes albopictus.Parasit Vectors. 2015 Sep 17;8:464. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-1070-4. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 26384002 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical nucleators are dispensable for stress granule assembly in Drosophila intestinal progenitors.J Cell Sci. 2020 May 18;133(10):jcs243451. doi: 10.1242/jcs.243451. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32265270 Free PMC article.
-
Germ Cell Lineage Homeostasis in Drosophila Requires the Vasa RNA Helicase.Genetics. 2019 Nov;213(3):911-922. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302558. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31484689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lantz V, Ambrosio L, Schedl P (1992) The Drosophila orb gene is predicted to encode sex-specific germline RNA-binding proteins and has localized transcripts in ovaries and early embryos. Development 115: 75–88. - PubMed
-
- Lantz V, Chang JS, Horabin JI, Bopp D, Schedl P (1994) The Drosophila orb RNA-binding protein is required for the formation of the egg chamber and establishment of polarity. Genes Dev 8: 598–613. - PubMed
-
- Hake LE, Richter JD (1994) CPEB is a specificity factor that mediates cytoplasmic polyadenylation during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Cell 79: 617–627. - PubMed
-
- Richter JD (2007) CPEB: a life in translation. Trends Biochem Sci 32: 279–285. - PubMed
-
- Keleman K, Krutner S, Alenius M, Dickson BJ (2007) Function of the Drosophila CPEB protein Orb2 in long-term courtship memory. Nat Neurosci 10: 1587–1593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

