The FEAR protein Slk19 restricts Cdc14 phosphatase to the nucleus until the end of anaphase, regulating its participation in mitotic exit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 24039885
- PMCID: PMC3769316
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073194
The FEAR protein Slk19 restricts Cdc14 phosphatase to the nucleus until the end of anaphase, regulating its participation in mitotic exit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
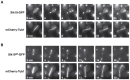
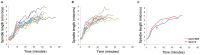
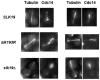
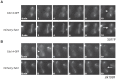
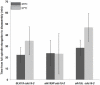
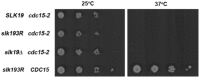
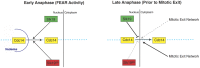
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitosis, the protein Slk19 plays an important role in the initial release of Cdc14 phosphatase from the nucleolus to the nucleus in early anaphase, an event that is critical for proper anaphase progression. A role for Slk19 in later mitotic stages of Cdc14 regulation, however, has not been demonstrated. While investigating the role of Slk19 post-translational modification on Cdc14 regulation, we found that a triple point mutant of SLK19, slk19(3R) (three lysine-to-arginine mutations), strongly affects Cdc14 localization during late anaphase and mitotic exit. Using fluorescence live-cell microscopy, we found that, similar to slk19Δ cells, slk19(3R) cells exhibit no defect in spindle stability and only a mild defect in spindle elongation dynamics. Unlike slk19Δcells, however, slk19(3R) cells exhibit no defect in Cdc14 release from the nucleolus to the nucleus. Instead, slk19(3R) cells are defective in the timing of Cdc14 movement from the nucleus to the cytoplasm at the end of anaphase. This mutant has a novel phenotype: slk19(3R) causes premature Cdc14 movement to the cytoplasm prior to, rather than concomitant with, spindle disassembly. One consequence of this premature Cdc14 movement is the inappropriate activation of the mitotic exit network, made evident by the fact that slk19(3R) partially rescues a mutant of the mitotic exit network kinase Cdc15. In conclusion, in addition to its role in regulating Cdc14 release from the nucleolus to the nucleus, we found that Slk19 is also important for regulating Cdc14 movement from the nucleus to the cytoplasm at the end of anaphase.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cdc14 Early Anaphase Release, FEAR, Is Limited to the Nucleus and Dispensable for Efficient Mitotic Exit.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):e0128604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128604. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26090959 Free PMC article.
-
FEAR but not MEN genes are required for exit from meiosis I.Cell Cycle. 2005 Aug;4(8):1093-8. Epub 2005 Aug 23. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15970684
-
The Polo-like kinase Cdc5 interacts with FEAR network components and Cdc14.Cell Cycle. 2008 Oct;7(20):3262-72. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.20.6852. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18927509 Free PMC article.
-
Assembling the spindle midzone in the right place at the right time.Cell Cycle. 2008 Feb 1;7(3):283-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.3.5349. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18235228 Review.
-
At the interface between signaling and executing anaphase--Cdc14 and the FEAR network.Genes Dev. 2004 Nov 1;18(21):2581-95. doi: 10.1101/gad.1247304. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15520278 Review.
Cited by
-
Slk19 enhances cross-linking of microtubules by Ase1 and Stu1.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Nov 1;32(21):ar22. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-05-0279. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34495712 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Novel Functions of the Small GTPase Ypt1p under Heat-Shock by Characterizing a Temperature-Sensitive Mutant Yeast Strain, ypt1-G80D.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 1;20(1):132. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010132. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30609659 Free PMC article.
-
Outer kinetochore protein Dam1 promotes centromere clustering in parallel with Slk19 in budding yeast.Chromosoma. 2019 Jun;128(2):133-148. doi: 10.1007/s00412-019-00694-9. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Chromosoma. 2019. PMID: 30903360
-
Regulation of kinetochore configuration during mitosis.Curr Genet. 2018 Dec;64(6):1197-1203. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0841-9. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29704052 Review.
References
-
- Visintin R, Craig K, Hwang ES, Prinz S, Tyers M, et al. (1998) The phosphatase Cdc14 triggers mitotic exit by reversal of Cdk-dependent phosphorylation. Mol Cell 2: 709–18. - PubMed
-
- Stegmeier F, Amon A (2004) Closing mitosis: the functions of the Cdc14 phosphatase and its regulation. Annu Rev Genet 38: 203–32. - PubMed
-
- Shou W, Seol JH, Shevchenko A, Baskerville C, Moazed D, et al. (1999) Exit from mitosis is triggered by Tem1-dependent release of the protein phosphatase Cdc14 from nucleolar RENT complex. Cell 97(2): 233–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

