The long non-coding RNA Fendrr links epigenetic control mechanisms to gene regulatory networks in mammalian embryogenesis
- PMID: 24036695
- PMCID: PMC3866236
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.26165
The long non-coding RNA Fendrr links epigenetic control mechanisms to gene regulatory networks in mammalian embryogenesis
Abstract
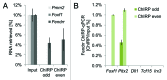
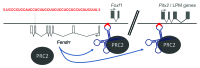
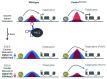
Epigenetic control mechanisms determine active and silenced regions of the genome. It is known that the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) and the Trithorax group/Mixed lineage leukemia (TrxG/Mll) complex are able to set repressive and active histone marks, respectively. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) can interact with either of these complexes and guide them to regulatory elements, thereby modifying the expression levels of target genes. The lncRNA Fendrr is transiently expressed in lateral mesoderm of mid-gestational mouse embryos and was shown to interact with both PRC2 and TrxG/Mll complexes in vivo. Gene targeting revealed that loss of Fendrr results in impaired differentiation of tissues derived from lateral mesoderm, the heart and the body wall, ultimately leading to embryonic death. Molecular data suggests that Fendrr acts via dsDNA/RNA triplex formation at target regulatory elements, and directly increases PRC2 occupancy at these sites. This, in turn, modifies the ratio of repressive to active marks, adjusting the expression levels of Fendrr target genes in lateral mesoderm. We propose that Fendrr also mediates long-term epigenetic marks to define expression levels of its target genes within the descendants of lateral mesoderm cells. Here we discuss approaches for lncRNA gene knockouts in the mouse, and suggest a model how Fendrr and possibly other lncRNAs act during embryogenesis.
Keywords: Fendrr; Polycomb Repressive Complex 2; embryogenesis; epigenetic control; histone modification; lncRNA; long non-coding RNA; mouse.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The tissue-specific lncRNA Fendrr is an essential regulator of heart and body wall development in the mouse.Dev Cell. 2013 Jan 28;24(2):206-14. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.12.012. Dev Cell. 2013. PMID: 23369715 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-coding RNA FENDRR Modulates Autophagy Through Epigenetic Suppression of ATG7 via Binding PRC2 in Acute Pancreatitis.Inflammation. 2021 Jun;44(3):999-1013. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01395-7. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33417179
-
Fendrr synergizes with Wnt signalling to regulate fibrosis related genes during lung development via its RNA:dsDNA triplex element.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jul 7;51(12):6227-6237. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad395. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37207329 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA FENDRR: Gene Structure, Expression, and Biological Relevance.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jan 27;12(2):177. doi: 10.3390/genes12020177. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33513839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of LncRNA FENDRR in Multiple Cancers: A Review.Curr Mol Med. 2023 May 30;23(7):606-629. doi: 10.2174/1566524022666220509122505. Curr Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 35579154 Review.
Cited by
-
The biological function and potential mechanism of long non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(22):12900-12909. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15968. Epub 2020 Oct 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33052009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non coding RNA NRON inhibited breast cancer development through regulating miR-302b/SRSF2 axis.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Aug 15;12(8):4683-4692. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32913541 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA FENDRR inhibits the stemenss of colorectal cancer cells through directly binding to Sox2 RNA.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):8698-8708. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1977054. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34697986 Free PMC article.
-
An HGF-dependent positive feedback loop between bladder cancer cells and fibroblasts mediates lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023 Dec;43(12):1289-1311. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12470. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37483113 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNAs in vertebrates: advances and challenges.Biochimie. 2015 Oct;117:3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25812751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mahlapuu M, Ormestad M, Enerbäck S, Carlsson P. The forkhead transcription factor Foxf1 is required for differentiation of extra-embryonic and lateral plate mesoderm. Development. 2001;128:155–66. - PubMed
-
- Mahlapuu M, Enerbäck S, Carlsson P. Haploinsufficiency of the forkhead gene Foxf1, a target for sonic hedgehog signaling, causes lung and foregut malformations. Development. 2001;128:2397–406. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
