Oncolytic adenovirus encoding tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) inhibits the growth and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 24025362
- PMCID: PMC3925656
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.26043
Oncolytic adenovirus encoding tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) inhibits the growth and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
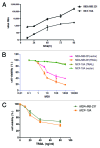
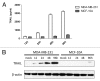
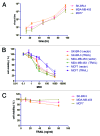
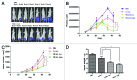
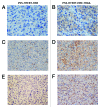
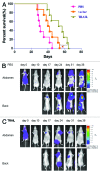
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising cancer therapeutic target due to its selective apoptosis-inducing effect in cancer cells. To efficiently deliver TRAIL to the tumor cells, an oncolytic adenovirus (p55-hTERT-HRE-TRAIL) carrying the TRAIL coding sequence was constructed. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the effect of p55-hTERT-HRE-TRAIL on the growth and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). We observed that infection of the recombinant adenovirus resulted in expression of TRAIL and massive cell death in a TNBC cell line MDA-MB-231. This effect is much weaker in MCF-10A, which is a normal breast cell line. Administration of P55-HTERT-HRE-TRAIL significantly reduced orthotopic breast tumor growth and extended survival in a metastatic model. Our results suggest the oncolytic adenovirus armed with P55-HTERT-HRE-TRAIL, which exhibited enhanced anti-tumor activity and improved survival, is a promising candidate for virotherapy of TNBC.
Keywords: adenovirus; triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC); tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL); virotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing of Mcl-1 overcomes resistance of melanoma cells against TRAIL-armed oncolytic adenovirus by enhancement of apoptosis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Sep;99(9):1279-1291. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02081-3. Epub 2021 May 24. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34028599 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced antitumor effect of combining TRAIL and MnSOD mediated by CEA-controlled oncolytic adenovirus in lung cancer.Cancer Gene Ther. 2016 Jun;23(6):168-77. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2016.11. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016. PMID: 27080225
-
Targeting lung cancer stem-like cells with TRAIL gene armed oncolytic adenovirus.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 May;19(5):915-23. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12397. Epub 2015 Feb 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25683371 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting TRAIL Death Receptors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers: Challenges and Strategies for Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2022 Nov 22;11(23):3717. doi: 10.3390/cells11233717. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36496977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Oct;70(19):3617-29. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1264-x. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23329170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trial Watch-Oncolytic viruses and cancer therapy.Oncoimmunology. 2015 Dec 8;5(2):e1117740. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1117740. eCollection 2016 Feb. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 27057469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TRAIL system is over-expressed in breast cancer and FLIP a marker of good prognosis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Mar;141(3):505-14. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1822-0. Epub 2014 Sep 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25230899
-
Trial Watch:: Oncolytic viruses for cancer therapy.Oncoimmunology. 2014 Jun 1;3:e28694. doi: 10.4161/onci.28694. eCollection 2014. Oncoimmunology. 2014. PMID: 25097804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCL12 Retargeting of an Oncolytic Adenovirus Vector to the Chemokine CXCR4 and CXCR7 Receptors in Breast Cancer.J Cancer Ther. 2021 Jun;12(6):311-336. doi: 10.4236/jct.2021.126029. J Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 34178415 Free PMC article.
-
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Basic Biology and Immuno-Oncolytic Viruses.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 21;15(8):2393. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082393. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190321 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer. 2007;109:1721–8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22618. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
