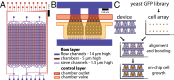
A chemostat array enables the spatio-temporal analysis of the yeast proteome
- PMID: 24019481
- PMCID: PMC3785771
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1308265110
A chemostat array enables the spatio-temporal analysis of the yeast proteome
Abstract
Observing cellular responses to perturbations is central to generating and testing hypotheses in biology. We developed a massively parallel microchemostat array capable of growing and observing 1,152 yeast-GFP strains on the single-cell level with 20 min time resolution. We measured protein abundance and localization changes in 4,085 GFP-tagged strains in response to methyl methanesulfonate and analyzed 576 GFP strains in five additional conditions for a total of more than 10,000 unique experiments, providing a systematic view of the yeast proteome in flux. We observed that processing bodies formed rapidly and synchronously in response to UV irradiation, and in conjunction with 506 deletion-GFP strains, identified four gene disruptions leading to abnormal ribonucleotide-diphosphate reductase (Rnr4) localization. Our microchemostat platform enables the large-scale interrogation of proteomes in flux and permits the concurrent observation of protein abundance, localization, cell size, and growth parameters on the single-cell level for thousands of microbial cultures in one experiment.
Keywords: DNA damage response; cell arrays; high-content imaging; microfluidics; yeast proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
 ,
,  for linear data;
for linear data;  ,
,  for log-transformed data;
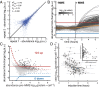
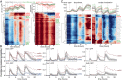
for log-transformed data;  , Spearman correlation coefficient; n, number of data points). (B) Mean abundance for 2,534 strains. Abundance is normalized to the median of the pre-MMS data points. The orange line shows the global median. The red and blue lines represent a threefold increase/decrease threshold. (C) Abundance fold change vs. pre-MMS abundance. The gray scale shows the significance of the fold change for each protein. Dashed lines show the P = 0.01 significance threshold. A total of 124 proteins fell above both significance thresholds (P value <0.01 and fold change >3). (D) Protein accumulation rate plotted vs. induction time for the 124 up-regulated proteins. SDs are shown with gray lines (n varies from 1 to 16). (Inset) Correlation between protein timing and mRNA timing.
, Spearman correlation coefficient; n, number of data points). (B) Mean abundance for 2,534 strains. Abundance is normalized to the median of the pre-MMS data points. The orange line shows the global median. The red and blue lines represent a threefold increase/decrease threshold. (C) Abundance fold change vs. pre-MMS abundance. The gray scale shows the significance of the fold change for each protein. Dashed lines show the P = 0.01 significance threshold. A total of 124 proteins fell above both significance thresholds (P value <0.01 and fold change >3). (D) Protein accumulation rate plotted vs. induction time for the 124 up-regulated proteins. SDs are shown with gray lines (n varies from 1 to 16). (Inset) Correlation between protein timing and mRNA timing.
Similar articles
-
Proteome-wide screens in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using the yeast GFP collection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;736:169-78. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7210-1_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22161327
-
A novel single-cell screening platform reveals proteome plasticity during yeast stress responses.J Cell Biol. 2013 Mar 18;200(6):839-50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201301120. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23509072 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic High-Content Screening of Fluorescently Tagged Yeast Double Mutant Strains.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2381:57-78. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1740-3_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34590270
-
Mapping the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Spatial Proteome with High Resolution Using hyperLOPIT.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2049:165-190. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9736-7_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31602611
-
Localizing the proteome.Genome Biol. 2003;4(12):240. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-12-240. Epub 2003 Nov 18. Genome Biol. 2003. PMID: 14659010 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-molecule bioelectronics.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2015 Jul-Aug;7(4):475-93. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1323. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25529538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proximity-Dependent Biotinylation Approaches to Explore the Dynamic Compartmentalized Proteome.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Mar 4;9:852911. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.852911. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35309513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heritability and genetic basis of protein level variation in an outbred population.Genome Res. 2014 Aug;24(8):1363-70. doi: 10.1101/gr.170506.113. Epub 2014 May 13. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 24823668 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput single-cell analysis for the proteomic dynamics study of the yeast osmotic stress response.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 9;7:42200. doi: 10.1038/srep42200. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28181485 Free PMC article.
-
TheCellVision.org: A Database for Visualizing and Mining High-Content Cell Imaging Projects.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Nov 5;10(11):3969-3976. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401570. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32934016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giepmans BN, Adams SR, Ellisman MH, Tsien RY. The fluorescent toolbox for assessing protein location and function. Science. 2006;312(5771):217–224. - PubMed
-
- Cohen AA, et al. Dynamic proteomics of individual cancer cells in response to a drug. Science. 2008;322(5907):1511–1516. - PubMed
-
- Newman JR, et al. Single-cell proteomic analysis of S. cerevisiae reveals the architecture of biological noise. Nature. 2006;441(7095):840–846. - PubMed
-
- Huh WK, et al. Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature. 2003;425(6959):686–691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

