Characterization of oxygen radical formation mechanism at early cardiac ischemia
- PMID: 24008731
- PMCID: PMC3789172
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.313
Characterization of oxygen radical formation mechanism at early cardiac ischemia
Abstract
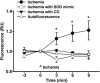
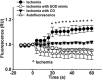
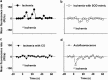
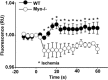
Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) causes severe cardiac damage. Although the primary function of oxymyoglobin (Mb) has been considered to be cellular O2 storage and supply, previous research has suggested that Mb is a potentially protective element against I/R injury. However, the mechanism of its protective action is still largely unknown. With a real-time fluorescent technique, we observed that at the onset of ischemia, there was a small burst of superoxide (O2(•-)) release, as visualized in an isolated rat heart. Thus, we hypothesize that the formation of O2(•-) correlates to Mb due to a decrease in oxygen tension in the myocardium. Measurement of O2(•-) production in a Langendorff apparatus was performed using surface fluorometry. An increase in fluorescence was observed during the onset of ischemia in hearts perfused with a solution of hydroethidine, a fluorescent dye sensitive to intracellular O2(•-). The increase of fluorescence in the ischemic heart was abolished by a superoxide dismutase mimic, carbon monoxide, or by Mb-knockout gene technology. Furthermore, we identified that O2(•-) was not generated from the intracellular endothelium but from the myocytes, which are a rich source of Mb. These results suggest that during the onset of ischemia, Mb is responsible for generating O2(•-). This novel mechanism may shed light on the protective role of Mb in I/R injury.
Figures
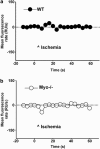
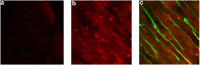
Similar articles
-
Role of myoglobin in the antioxidant defense of the heart.FASEB J. 2004 Jul;18(10):1156-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-1382fje. Epub 2004 May 7. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15132981
-
Role of superoxide production in post-ischemic cardiac dysfunction and norepinephrine overflow in rat hearts.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Jul 5;711(1-3):36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 Apr 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23628722
-
Endogenous sulfur dioxide aggravates myocardial injury in isolated rat heart with ischemia and reperfusion.Transplantation. 2009 Feb 27;87(4):517-24. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318195fe82. Transplantation. 2009. PMID: 19307787
-
Cellular response to reperfused oxygen in the postischemic myocardium.Am J Physiol. 1996 Aug;271(2 Pt 2):H687-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1996.271.2.H687. Am J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8770112
-
Biological plausibility for carbon monoxide as a copollutant in PM epidemiologic studies.Inhal Toxicol. 2000;12 Suppl 4:91-107. doi: 10.1080/089583700750019521. Inhal Toxicol. 2000. PMID: 12881888 Review.
Cited by
-
Criteria air pollutants and hospitalizations of a wide spectrum of cardiovascular diseases: A nationwide case-crossover study in China.Eco Environ Health. 2022 Nov 17;1(4):204-211. doi: 10.1016/j.eehl.2022.10.002. eCollection 2022 Dec. Eco Environ Health. 2022. PMID: 38077257 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione infusion before primary percutaneous coronary intervention: a randomised controlled pilot study.BMJ Open. 2019 Aug 8;9(8):e025884. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025884. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31399448 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Redox Roles of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 20;16(11):27770-80. doi: 10.3390/ijms161126059. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26610475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects of 6-Gingerol on Cardiotoxicity Induced by Arsenic Trioxide Through AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 28;13:868393. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.868393. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35571130 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effects of Melatonin in the Ovarian Transport Medium on In Vitro Embryo Production of Iberian Red Deer (Cervus elaphus hispanicus).Animals (Basel). 2020 Apr 27;10(5):763. doi: 10.3390/ani10050763. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32349425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zuo L, Chen YR, Reyes LA, Lee HL, Chen CL, Villamena FA, et al. The radical trap 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide exerts dose-dependent protection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through preservation of mitochondrial electron transport. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;329:515–523. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zuo L, Roberts WJ, Tolomello RC, Goins AT. Ischemic and hypoxic preconditioning protect cardiac muscles via intracellular ROS signaling. Front Biol. 2013;8:305–311.
-
- Galaris D, Eddy L, Arduini A, Cadenas E, Hochstein P. Mechanisms of reoxygenation injury in myocardial infarction: implications of a myoglobin redox cycle. Biochemi Biophy Res Commun. 1989;160:1162–1168. - PubMed
-
- Galaris D, Cadenas E, Hochstein P. Redox cycling of myoglobin and ascorbate: a potential protective mechanism against oxidative reperfusion injury in muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989;273:497–504. - PubMed
-
- Ordway GA, Garry DJ. Myoglobin: an essential hemoprotein in striated muscle. J Exp Biol. 2004;207 (Pt 20:3441–3446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

