Sec16 influences transitional ER sites by regulating rather than organizing COPII
- PMID: 24006484
- PMCID: PMC3814151
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E13-04-0185
Sec16 influences transitional ER sites by regulating rather than organizing COPII
Abstract
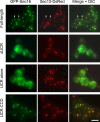
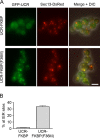
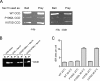
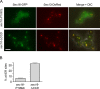
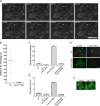
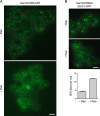
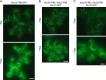
During the budding of coat protein complex II (COPII) vesicles from transitional endoplasmic reticulum (tER) sites, Sec16 has been proposed to play two distinct roles: negatively regulating COPII turnover and organizing COPII assembly at tER sites. We tested these ideas using the yeast Pichia pastoris. Redistribution of Sec16 to the cytosol accelerates tER dynamics, supporting a negative regulatory role for Sec16. To evaluate a possible COPII organization role, we dissected the functional regions of Sec16. The central conserved domain, which had been implicated in coordinating COPII assembly, is actually dispensable for normal tER structure. An upstream conserved region (UCR) localizes Sec16 to tER sites. The UCR binds COPII components, and removal of COPII from tER sites also removes Sec16, indicating that COPII recruits Sec16 rather than the other way around. We propose that Sec16 does not in fact organize COPII. Instead, regulation of COPII turnover can account for the influence of Sec16 on tER sites.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sec16 is a determinant of transitional ER organization.Curr Biol. 2005 Aug 23;15(16):1439-47. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.06.065. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16111939
-
Sec12 binds to Sec16 at transitional ER sites.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31156. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031156. Epub 2012 Feb 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22347445 Free PMC article.
-
Organisation of human ER-exit sites: requirements for the localisation of Sec16 to transitional ER.J Cell Sci. 2009 Aug 15;122(Pt 16):2924-34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.044032. Epub 2009 Jul 28. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19638414 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast GRASP Grh1 colocalizes with COPII and is dispensable for organizing the secretory pathway.Traffic. 2010 Sep;11(9):1168-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01089.x. Epub 2010 Jun 21. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20573068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of coat assembly--sorting things out at the ER.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;22(4):447-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 May 1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20439155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual function of cTAGE5 in collagen export from the endoplasmic reticulum.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jul 1;27(13):2008-13. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-03-0180. Epub 2016 May 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27170179 Free PMC article.
-
Sec16 alternative splicing dynamically controls COPII transport efficiency.Nat Commun. 2016 Aug 5;7:12347. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12347. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27492621 Free PMC article.
-
Sar1 localizes at the rims of COPII-coated membranes in vivo.J Cell Sci. 2016 Sep 1;129(17):3231-7. doi: 10.1242/jcs.189423. Epub 2016 Jul 18. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27432890 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated point mutations improve α-amylase secretion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Yeast Res. 2022 Jul 15;22(1):foac033. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foac033. FEMS Yeast Res. 2022. PMID: 35776981 Free PMC article.
-
A sophisticated, differentiated Golgi in the ancestor of eukaryotes.BMC Biol. 2018 Mar 7;16(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12915-018-0492-9. BMC Biol. 2018. PMID: 29510703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonny B, Madden D, Hamamoto S, Orci L, Schekman R. Dynamics of the COPII coat with GTO and stable analogues. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:531–537. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Schekman R. SEC12 encodes a guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor essential for transport vesicle budding from the ER. Nature. 1993;365:347–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

