HDL induces the expression of the M2 macrophage markers arginase 1 and Fizz-1 in a STAT6-dependent process
- PMID: 23991225
- PMCID: PMC3749183
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074676
HDL induces the expression of the M2 macrophage markers arginase 1 and Fizz-1 in a STAT6-dependent process
Abstract
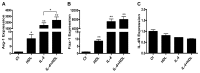
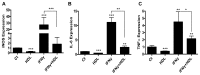
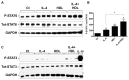
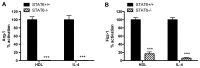
Our lab has previously shown in a mouse model that normalization of a low HDL level achieves atherosclerotic plaque regression. This included the shift from a pro ("M1") to an anti-inflammatory ("M2") phenotypic state of plaque macrophages. Whether HDL can directly cause this phenotypic change and, if so, what the signaling mechanism is, were explored in the present studies. Murine primary macrophages treated with HDL showed increased gene expression for the M2 markers Arginase-1 (Arg-1) and Fizz-1, which are classically induced by IL-4. HDL was able to potentiate the IL-4-induced changes in Arg-1, and tended to do the same for Fizz-1, while suppressing the expression of inflammatory genes in response to IFNγ. The effects of either IL-4 or HDL were suppressed when macrophages were from STAT6(-/-) mice, but inhibitor studies suggested differential utilization of JAK isoforms by IL-4 and HDL to activate STAT6 by phosphorylation. Overall, our results describe a new function of HDL, namely its ability to directly enrich macrophages in markers of the M2, anti-inflammatory, state in a process requiring STAT6.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pyropia yezoensis glycoprotein promotes the M1 to M2 macrophage phenotypic switch via the STAT3 and STAT6 transcription factors.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Aug;38(2):666-74. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2656. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27353313
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 enhances atherosclerotic plaque stability by skewing macrophages to the M2 phenotype.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Jan;22(1):409-416. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13329. Epub 2017 Sep 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 28944992 Free PMC article.
-
CDK8/19 inhibitor enhances arginase-1 expression in macrophages via STAT6 and p38 MAPK activation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 15;979:176852. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176852. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39067565
-
High-density lipoprotein immunomodulates the functional activities of macrophage and cytokines produced during ex vivo macrophage-CD4+ T cell crosstalk at the recent-onset human type 1 diabetes.Cytokine. 2017 Aug;96:59-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Cytokine. 2017. PMID: 28324804
-
STAT6 Upregulation Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization to Suppress Atherosclerosis.Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2017 Jun 15;23:240-249. doi: 10.12659/msmbr.904014. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2017. PMID: 28615615 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP) Activates Macrophages and Promotes Liver Fibrosis in Schistosoma japonicum-Infected Mice.J Immunol Res. 2019 Dec 1;2019:5148575. doi: 10.1155/2019/5148575. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31886304 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Characterization of Free-Floating 3D Macrophage Programming Model in the Presence of Cancer Cell Spheroids.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 28;24(13):10763. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310763. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445941 Free PMC article.
-
High-density lipoproteins put out the fire.Cell Metab. 2014 Feb 4;19(2):175-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.01.009. Cell Metab. 2014. PMID: 24506861 Free PMC article.
-
ADAM17 Boosts Cholesterol Efflux and Downstream Effects of High-Density Lipoprotein on Inflammatory Pathways in Macrophages.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 Jun;41(6):1854-1873. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.315145. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33882688 Free PMC article.
-
The Pivotal Immunoregulatory Functions of Microglia and Macrophages in Glioma Pathogenesis and Therapy.J Oncol. 2022 Apr 4;2022:8903482. doi: 10.1155/2022/8903482. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35419058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moore KJ, Tabas I (2011) Macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell 145: 341-355. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.04.005. PubMed: 21529710. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reis ED, Li J, Fayad ZA, Rong JX, Hansoty D et al. (2001) Dramatic remodeling of advanced atherosclerotic plaques of the apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse in a novel transplantation model. J Vasc Surg 34: 541-547. doi:10.1067/mva.2001.115963. PubMed: 11533609. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Llodrá J, Angeli V, Liu J, Trogan E, Fisher EA et al. (2004) Emigration of monocyte-derived cells from atherosclerotic lesions characterizes regressive, but not progressive, plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101: 11779-11784. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403259101. PubMed: 15280540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feig JE, Rong JX, Shamir R, Sanson M, Vengrenyuk Y et al. (2011) HDL promotes rapid atherosclerosis regression in mice and alters inflammatory properties of plaque monocyte-derived cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 7166-7171. doi:10.1073/pnas.1016086108. PubMed: 21482781. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

