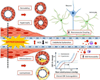
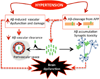
Hypertension: a harbinger of stroke and dementia
- PMID: 23980072
- PMCID: PMC3847558
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.01063
Hypertension: a harbinger of stroke and dementia
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Leukoaraiosis: the brain under pressure: target for treatment?Neurology. 2005 Jun 14;64(11):1832-3. doi: 10.1212/wnl.64.11.1832. Neurology. 2005. PMID: 15955929 No abstract available.
-
[Hypertension and the brain].Ugeskr Laeger. 2009 Jun 8;171(24):2025-8. Ugeskr Laeger. 2009. PMID: 19523368 Danish.
-
Blood pressure and treatment of persons with hypertension as it relates to cognitive outcomes including executive function.J Am Soc Hypertens. 2012 Sep-Oct;6(5):309-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2012.08.004. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 22995799 Review. No abstract available.
-
Perspective: silent, but preventable, perils.Nature. 2014 Jun 26;510(7506):S12. doi: 10.1038/510S12a. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24964022 No abstract available.
-
Hypertension and Dementia: Epidemiological and Experimental Evidence Revealing a Detrimental Relationship.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Mar 8;17(3):347. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030347. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27005613 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapies to Reduce Blood Pressure Acutely.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016 Jun;18(6):43. doi: 10.1007/s11906-016-0651-8. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016. PMID: 27125389 Review.
-
Prevalence of Depression in Patients With Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Aug;94(31):e1317. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001317. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26252317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secondary Stroke Prevention: Improving Diagnosis and Management with Newer Technologies.Transl Stroke Res. 2016 Dec;7(6):458-477. doi: 10.1007/s12975-016-0494-2. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Transl Stroke Res. 2016. PMID: 27586681 Review.
-
Vasculo-Neuronal Coupling and Neurovascular Coupling at the Neurovascular Unit: Impact of Hypertension.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 25;11:584135. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.584135. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33101063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarcopenia and diabetes-induced dementia risk.Brain Commun. 2023 Dec 20;6(1):fcad347. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcad347. eCollection 2024. Brain Commun. 2023. PMID: 38179233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Feigin VL, Rodgers A. Blood pressure and stroke: an overview of published reviews. Stroke. 2004;35:1024. - PubMed
-
- Scuteri A, Nilsson PM, Tzourio C, Redon J, Laurent S. Microvascular brain damage with aging and hypertension: pathophysiological consideration and clinical implications. J Hypertens. 2011;29:1469–1477. - PubMed
-
- Mulvany MJ. Small artery remodelling in hypertension. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012;110:49–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

