Identification and characterization of multiple TRIM proteins that inhibit hepatitis B virus transcription
- PMID: 23936368
- PMCID: PMC3731306
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070001
Identification and characterization of multiple TRIM proteins that inhibit hepatitis B virus transcription
Abstract
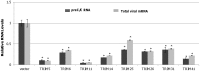
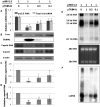
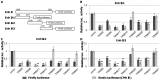
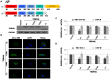
Tripartite motif (TRIM) proteins constitute a family of over 100 members that share conserved tripartite motifs and exhibit diverse biological functions. Several TRIM proteins have been shown to restrict viral infections and regulate host cellular innate immune responses. In order to identify TRIM proteins that modulate the infection of hepatitis B virus (HBV), we tested 38 human TRIMs for their effects on HBV gene expression, capsid assembly and DNA synthesis in human hepatoma cells (HepG2). The study revealed that ectopic expression of 8 TRIM proteins in HepG2 cells potently reduced the amounts of secreted HBV surface and e antigens as well as intracellular capsid and capsid DNA. Mechanistic analyses further demonstrated that the 8 TRIMs not only reduced the expression of HBV mRNAs, but also inhibited HBV enhancer I and enhancer II activities. Studies focused on TRIM41 revealed that a HBV DNA segment spanning nucleotide 1638 to nucleotide 1763 was essential for TRIM41-mediated inhibition of HBV enhancer II activity and the inhibitory effect depended on the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of TRIM41 as well as the integrity of TRIM41 C-terminal domain. Moreover, knockdown of endogenous TRIM41 in a HepG2-derived stable cell line significantly increased the level of HBV preC/C RNA, leading to an increase in viral core protein, capsid and capsid DNA. Our studies have thus identified eight TRIM proteins that are able to inhibit HBV transcription and provided strong evidences suggesting the endogenous role of TRIM41 in regulating HBV transcription in human hepatoma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tripartite Motif-Containing Protein 65 (TRIM65) Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Transcription.Viruses. 2024 May 31;16(6):890. doi: 10.3390/v16060890. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932182 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-26b inhibits hepatitis B virus transcription and replication by targeting the host factor CHORDC1 protein.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 12;289(50):35029-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.589978. Epub 2014 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25342750 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopetrosis-Associated Transmembrane Protein 1 Recruits RNA Exosome To Restrict Hepatitis B Virus Replication.J Virol. 2020 May 18;94(11):e01800-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01800-19. Print 2020 May 18. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32188736 Free PMC article.
-
TRIMmunity: the roles of the TRIM E3-ubiquitin ligase family in innate antiviral immunity.J Mol Biol. 2014 Mar 20;426(6):1265-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.12.005. Epub 2013 Dec 12. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24333484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TRIMendous Role of TRIMs in Virus-Host Interactions.Vaccines (Basel). 2017 Aug 22;5(3):23. doi: 10.3390/vaccines5030023. Vaccines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28829373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
When Hepatitis B Virus Meets Interferons.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jul 18;9:1611. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01611. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30072974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interaction of hepatitis B virus with the ubiquitin proteasome system in viral replication and associated pathogenesis.Virol J. 2019 May 30;16(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1183-z. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31146743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I IFN augments IL-27-dependent TRIM25 expression to inhibit HBV replication.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 Mar;15(3):272-281. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2016.67. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28194021 Free PMC article.
-
ROS/NF-κB Signaling Pathway-Mediated Transcriptional Activation of TRIM37 Promotes HBV-Associated Hepatic Fibrosis.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Aug 19;22:114-123. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.08.014. Online ahead of print. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32916597 Free PMC article.
-
Tripartite Motif-Containing Protein 65 (TRIM65) Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Transcription.Viruses. 2024 May 31;16(6):890. doi: 10.3390/v16060890. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hatakeyama S (2011) TRIM proteins and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 11: 792–804. - PubMed
-
- McNab FW, Rajsbaum R, Stoye JP, O’Garra A (2011) Tripartite-motif proteins and innate immune regulation. Curr Opin Immunol 23: 46–56. - PubMed
-
- Munir M (2010) TRIM proteins: another class of viral victims. Sci Signal 3: jc2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

