Roflumilast inhibits respiratory syncytial virus infection in human differentiated bronchial epithelial cells
- PMID: 23936072
- PMCID: PMC3720563
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069670
Roflumilast inhibits respiratory syncytial virus infection in human differentiated bronchial epithelial cells
Abstract
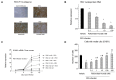
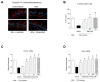
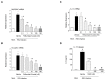
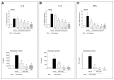
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes acute exacerbations in COPD and asthma. RSV infects bronchial epithelial cells (HBE) that trigger RSV associated lung pathology. This study explores whether the phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor Roflumilast N-oxide (RNO), alters RSV infection of well-differentiated HBE (WD-HBE) in vitro. WD-HBE were RSV infected in the presence or absence of RNO (0.1-100 nM). Viral infection (staining of F and G proteins, nucleoprotein RNA level), mRNA of ICAM-1, ciliated cell markers (digital high speed videomicroscopy, β-tubulin immunofluorescence, Foxj1 and Dnai2 mRNA), Goblet cells (PAS), mRNA of MUC5AC and CLCA1, mRNA and protein level of IL-13, IL-6, IL-8, TNFα, formation of H2O2 and the anti-oxidative armamentarium (mRNA of Nrf2, HO-1, GPx; total antioxidant capacity (TAC) were measured at day 10 or 15 post infection. RNO inhibited RSV infection of WD-HBE, prevented the loss of ciliated cells and markers, reduced the increase of MUC5AC and CLCA1 and inhibited the increase of IL-13, IL-6, IL-8, TNFα and ICAM-1. Additionally RNO reversed the reduction of Nrf2, HO-1 and GPx mRNA levels and consequently restored the TAC and reduced the H2O2 formation. RNO inhibits RSV infection of WD-HBE cultures and mitigates the cytopathological changes associated to this virus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Respiratory syncytial virus inhibits ciliagenesis in differentiated normal human bronchial epithelial cells: effectiveness of N-acetylcysteine.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048037. Epub 2012 Oct 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23118923 Free PMC article.
-
Roflumilast N-oxide, a PDE4 inhibitor, improves cilia motility and ciliated human bronchial epithelial cells compromised by cigarette smoke in vitro.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Aug;166(8):2243-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01929.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22385203 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro modeling of respiratory syncytial virus infection of pediatric bronchial epithelium, the primary target of infection in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 27;109(13):5040-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1110203109. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22411804 Free PMC article.
-
The preclinical pharmacology of roflumilast--a selective, oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor in development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Aug;23(4):235-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2010.03.011. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20381629 Review.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus interaction with human airway epithelium.Trends Microbiol. 2013 May;21(5):238-44. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.02.004. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Trends Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23523320 Review.
Cited by
-
Redox Biology of Respiratory Viral Infections.Viruses. 2018 Jul 26;10(8):392. doi: 10.3390/v10080392. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30049972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress and ROS-mediated cellular events in RSV infection: potential protective roles of antioxidants.Virol J. 2023 Oct 5;20(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02194-w. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 37798799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhaled Dual Phosphodiesterase 3/4 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Patients with COPD: A Short Review.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021 Aug 16;16:2363-2373. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S226688. eCollection 2021. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021. PMID: 34429594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene mutations in primary ciliary dyskinesia related to otitis media.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014 Mar;14(3):420. doi: 10.1007/s11882-014-0420-1. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014. PMID: 24459089 Review.
-
Virus-Induced Asthma Exacerbations: SIRT1 Targeted Approach.J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 13;9(8):2623. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082623. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32823491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nair H, Nokes DJ, Gessner BD, Dherani M, Madhi SA et al. (2010) Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 375(9725): 1545-1555. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60206-1. PubMed: 20399493. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hansbro NG, Horvat JC, Wark PA, Hansbro PM (2008) Understanding the mechanisms of viral induced asthma: new therapeutic directions. Pharmacol Ther 117: 313-353. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.11.002. PubMed: 18234348. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramaswamy M, Groskreutz DJ, Look DC (2009) Recognizing the importance of respiratory syncytial virus in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD 6: 64-75. doi:10.1080/15412550902724024. PubMed: 19229710. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee S, Lukacs NW (2010) Association of IL-13 in respiratory syncytial virus-induced pulmonary disease: still a promising target. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 8: 617-621. doi:10.1586/eri.10.39. PubMed: 20521887. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

