Tracking the engraftment and regenerative capabilities of transplanted lung stem cells using fluorescent nanodiamonds
- PMID: 23912062
- PMCID: PMC7097076
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2013.147
Tracking the engraftment and regenerative capabilities of transplanted lung stem cells using fluorescent nanodiamonds
Abstract
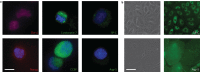
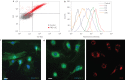
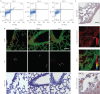
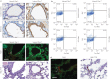
Lung stem/progenitor cells are potentially useful for regenerative therapy, for example in repairing damaged or lost lung tissue in patients. Several optical imaging methods and probes have been used to track how stem cells incorporate and regenerate themselves in vivo over time. However, these approaches are limited by photobleaching, toxicity and interference from background tissue autofluorescence. Here we show that fluorescent nanodiamonds, in combination with fluorescence-activated cell sorting, fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy and immunostaining, can identify transplanted CD45(-)CD54(+)CD157(+) lung stem/progenitor cells in vivo, and track their engraftment and regenerative capabilities with single-cell resolution. Fluorescent nanodiamond labelling did not eliminate the cells' properties of self-renewal and differentiation into type I and type II pneumocytes. Time-gated fluorescence imaging of tissue sections of naphthalene-injured mice indicates that the fluorescent nanodiamond-labelled lung stem/progenitor cells preferentially reside at terminal bronchioles of the lungs for 7 days after intravenous transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluorescent nanodiamonds enable quantitative tracking of human mesenchymal stem cells in miniature pigs.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 30;7:45607. doi: 10.1038/srep45607. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28358111 Free PMC article.
-
Wide-field imaging and flow cytometric analysis of cancer cells in blood by fluorescent nanodiamond labeling and time gating.Sci Rep. 2014 Jul 4;4:5574. doi: 10.1038/srep05574. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24994610 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent Nanoparticles for Noninvasive Stem Cell Tracking in Regenerative Medicine.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2018 Feb 1;14(2):240-256. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2018.2502. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 31352921 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Tracking the Transplanted Stem Cells Using Near-Infrared Fluorescent Nanoprobes: Turning from the First to the Second Near-Infrared Window.Adv Healthc Mater. 2018 Oct;7(20):e1800497. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201800497. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. PMID: 30019509 Review.
-
Noninvasive Tracking and Regenerative Capabilities of Transplanted Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Labeled with I-III-IV Semiconducting Nanocrystals in Liver-Injured Living Mice.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Mar 6;11(9):8763-8778. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b19953. Epub 2019 Feb 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 30741534
Cited by
-
Nanodiamonds in biomedical research: Therapeutic applications and beyond.PNAS Nexus. 2024 May 17;3(5):pgae198. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae198. eCollection 2024 May. PNAS Nexus. 2024. PMID: 38983694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving the creation of SiV centers in diamond via sub-μs pulsed annealing treatment.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 23;15(1):7251. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51523-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39179592 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the conformation of glycans and their interactions with proteins.J Biomed Sci. 2020 Sep 9;27(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00684-5. J Biomed Sci. 2020. PMID: 32900381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-coated nanodiamonds bind to autophagy receptors for entry into the selective autophagy pathway.Autophagy. 2017 Jan 2;13(1):187-200. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1254864. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 27846374 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence-Guided Probes of Aptamer-Targeted Gold Nanoparticles with Computed Tomography Imaging Accesses for in Vivo Tumor Resection.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 28;5:15675. doi: 10.1038/srep15675. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26507179 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

