Phased, secondary, small interfering RNAs in posttranscriptional regulatory networks
- PMID: 23881411
- PMCID: PMC3753373
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.114652
Phased, secondary, small interfering RNAs in posttranscriptional regulatory networks
Abstract
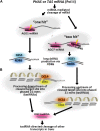
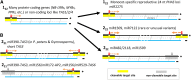
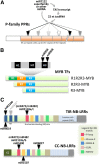
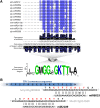
Plant genomes are the source of large numbers of small RNAs, generated via a variety of genetically separable pathways. Several of these pathways converge in the production of phased, secondary, small interfering RNAs (phasiRNAs), originally designated as trans-acting small interfering RNAs or tasiRNAs. PhasiRNA biogenesis requires the involvement of microRNAs as well as the cellular machinery for the production of siRNAs. PhasiRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana have been well described for their ability to function in trans to suppress target transcript levels. Plant genomic data from an expanding set of species have demonstrated that Arabidopsis is relatively sparing in its use of phasiRNAs, while other genomes contain hundreds or even thousands of phasiRNA-generating loci. In the dicots, targets of those phasiRNAs include several large or conserved families of genes, such as those encoding disease resistance proteins or transcription factors. Suppression of nucleotide-binding, leucine-rich repeat (NB-LRR) disease resistance genes by small RNAs is particularly unusual because of a high level of redundancy. In this review, we discuss plant phasiRNAs and the possible mechanistic significance of phasiRNA-based regulation of the NB-LRRs.
Figures
Comment in
-
The plant cell reviews aspects of microRNA and PhasiRNA regulatory function.Plant Cell. 2013 Jul;25(7):2382. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.250713. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23897925 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Extensive Families of miRNAs and PHAS Loci in Norway Spruce Demonstrate the Origins of Complex phasiRNA Networks in Seed Plants.Mol Biol Evol. 2015 Nov;32(11):2905-18. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv164. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Mol Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 26318183 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis of diverse plant phasiRNAs involves an miRNA-trigger and Dicer-processing.J Plant Res. 2017 Jan;130(1):17-23. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0878-0. Epub 2016 Nov 29. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27900550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB-LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans-acting siRNAs.Genes Dev. 2011 Dec 1;25(23):2540-53. doi: 10.1101/gad.177527.111. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 22156213 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide discovery and analysis of phased small interfering RNAs in Chinese sacred lotus.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 3;9(12):e113790. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113790. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25469507 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal regulation and roles of reproductive phasiRNAs in plants.Genes Genet Syst. 2022 Feb 23;96(5):209-215. doi: 10.1266/ggs.21-00042. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Genes Genet Syst. 2022. PMID: 34759068 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of virus-host interactions on plant response to abiotic stress.Plant Cell Rep. 2021 Nov;40(11):2225-2245. doi: 10.1007/s00299-021-02718-0. Epub 2021 May 29. Plant Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34050797 Review.
-
Small Non-Coding RNAs at the Crossroads of Regulatory Pathways Controlling Somatic Embryogenesis in Seed Plants.Plants (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;10(3):504. doi: 10.3390/plants10030504. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phased secondary small interfering RNAs in Camellia sinensis var. assamica.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023 Nov 24;5(4):lqad103. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqad103. eCollection 2023 Dec. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 38025046 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of small RNAs in pima (Gossypium barbadense L.).PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0116826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116826. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25679373 Free PMC article.
-
The plant cell reviews aspects of microRNA and PhasiRNA regulatory function.Plant Cell. 2013 Jul;25(7):2382. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.250713. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23897925 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adenot X., Elmayan T., Lauressergues D., Boutet S., Bouché N., Gasciolli V., Vaucheret H. (2006). DRB4-dependent TAS3 trans-acting siRNAs control leaf morphology through AGO7. Curr. Biol. 16: 927–932 - PubMed
-
- Allen E., Xie Z., Gustafson A.M., Carrington J.C. (2005). MicroRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121: 207–221 - PubMed
-
- Axtell M.J. (2013). Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 64: 137–159 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

