Activation of TRPV1 prevents OxLDL-induced lipid accumulation and TNF-α-induced inflammation in macrophages: role of liver X receptor α
- PMID: 23878415
- PMCID: PMC3710635
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/925171
Activation of TRPV1 prevents OxLDL-induced lipid accumulation and TNF-α-induced inflammation in macrophages: role of liver X receptor α
Abstract
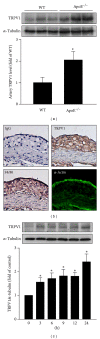
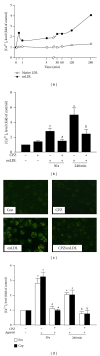
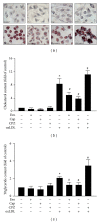
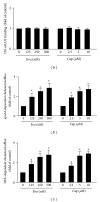
The transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) is crucial in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis; yet its role and underlying mechanism in the formation of macrophage foam cells remain unclear. Here, we show increased TRPV1 expression in the area of foamy macrophages in atherosclerotic aortas of apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Exposure of mouse bone-marrow-derived macrophages to oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) upregulated the expression of TRPV1. In addition, oxLDL activated TRPV1 and elicited calcium (Ca(2+)) influx, which were abrogated by the pharmacological TRPV1 antagonist capsazepine. Furthermore, oxLDL-induced lipid accumulation in macrophages was ameliorated by TRPV1 agonists but exacerbated by TRPV1 antagonist. Treatment with TRPV1 agonists did not affect the internalization of oxLDL but promoted cholesterol efflux by upregulating the efflux ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1. Moreover, the upregulation of ABC transporters was mainly through liver X receptor α-(LXRα-) dependent regulation of transcription. Moreover, the TNF-α-induced inflammatory response was alleviated by TRPV1 agonists but aggravated by the TRPV1 antagonist and LXR α siRNA in macrophages. Our data suggest that LXR α plays a pivotal role in TRPV1-activation-conferred protection against oxLDL-induced lipid accumulation and TNF-α-induced inflammation in macrophages.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The interaction of TRPV1 and lipids: Insights into lipid metabolism.Front Physiol. 2022 Dec 15;13:1066023. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1066023. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36589466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of soluble guanylyl cyclase prevents foam cell formation and atherosclerosis.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2014 Apr;210(4):799-810. doi: 10.1111/apha.12210. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2014. PMID: 24299003
-
UFM1 Protects Macrophages from oxLDL-Induced Foam Cell Formation Through a Liver X Receptor α Dependent Pathway.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2015;22(11):1124-40. doi: 10.5551/jat.28829. Epub 2015 Jun 4. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2015. PMID: 26040753
-
Molecular mechanism of curcumin on the suppression of cholesterol accumulation in macrophage foam cells and atherosclerosis.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012 May;56(5):691-701. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201100735. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012. PMID: 22648616
-
Targeting macrophages in atherosclerosis using nanocarriers loaded with liver X receptor agonists: A narrow review.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Mar 2;10:1147699. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1147699. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36936982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 Channel Involved in Atherosclerosis and Macrophage-Foam Cell Formation.Int J Biol Sci. 2016 May 25;12(7):812-23. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.15229. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27313495 Free PMC article.
-
TRP (transient receptor potential) ion channel family: structures, biological functions and therapeutic interventions for diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jul 5;8(1):261. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01464-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37402746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPV1 antagonism by capsazepine modulates innate immune response in mice infected with Plasmodium berghei ANKA.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:506450. doi: 10.1155/2014/506450. Epub 2014 Aug 24. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 25242870 Free PMC article.
-
B. vulgatus ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity through modulating intestinal serotonin synthesis and lipid absorption in mice.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2423040. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2423040. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39569932 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of TRPV1 and lipids: Insights into lipid metabolism.Front Physiol. 2022 Dec 15;13:1066023. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1066023. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36589466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glass CK, Witztum JL. Atherosclerosis: the road ahead. Cell. 2001;104(4):503–516. - PubMed
-
- Li AC, Glass CK. The macrophage foam cell as a target for therapeutic intervention. Nature Medicine. 2002;8(11):1235–1242. - PubMed
-
- Kunjathoor VV, Febbraio M, Podrez EA, et al. Scavenger receptors class A-I/II and CD36 are the principal receptors responsible for the uptake of modified low density lipoprotein leading to lipid loading in macrophages. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2002;277(51):49982–49988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

