Oxidant sensing by reversible disulfide bond formation
- PMID: 23861395
- PMCID: PMC3772196
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R113.462929
Oxidant sensing by reversible disulfide bond formation
Abstract
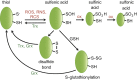
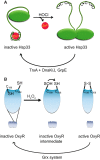
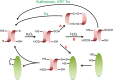
Maintenance of the cellular redox balance is crucial for cell survival. An increase in reactive oxygen, nitrogen, or chlorine species can lead to oxidative stress conditions, potentially damaging DNA, lipids, and proteins. Proteins are very sensitive to oxidative modifications, particularly methionine and cysteine residues. The reversibility of some of these oxidative protein modifications makes them ideally suited to take on regulatory roles in protein function. This is especially true for disulfide bond formation, which has the potential to mediate extensive yet fully reversible structural and functional changes, rapidly adjusting the protein's activity to the prevailing oxidant levels.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Oxidative Stress; Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS); Redox Signaling; Stress Response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidation of biological thiols by highly reactive disulfide-S-oxides.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2002 Mar;21(1):65-72. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2002. PMID: 12168727
-
Trapping redox partnerships in oxidant-sensitive proteins with a small, thiol-reactive cross-linker.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Dec;101:356-366. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.10.506. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27816612 Free PMC article.
-
Global methods to monitor the thiol-disulfide state of proteins in vivo.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006 May-Jun;8(5-6):763-72. doi: 10.1089/ars.2006.8.763. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006. PMID: 16771668 Review.
-
Protein redox modification as a cellular defense mechanism against tissue ischemic injury.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:343154. doi: 10.1155/2014/343154. Epub 2014 May 5. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014. PMID: 24883175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidoreduction of protein thiols in redox regulation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1378-81. doi: 10.1042/BST0331378. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246123 Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction of redox-sensitive cysteines using sequential distance and other sequence-based features.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Aug 24;17(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1185-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27553667 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine.Redox Biol. 2015;4:180-3. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 25588755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated plasma glypicans are associated with organ failure in patients with infection.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2019 Jan 7;7(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40635-018-0216-z. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2019. PMID: 30618011 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Thiol/Disulphide Homeostasis in Patients With Fibromyalgia.Arch Rheumatol. 2017 Jan 18;32(2):112-117. doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2017.5931. eCollection 2017 Jun. Arch Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 30375563 Free PMC article.
-
Different lanthanide elements induce strong gene expression changes in a lanthanide-accumulating methylotroph.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Dec 12;11(6):e0086723. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00867-23. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37909735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alam M. S., Garg S. K., Agrawal P. (2009) Studies on structural and functional divergence among seven WhiB proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. FEBS J. 276, 76–93 - PubMed
-
- Holmgren A., Johansson C., Berndt C., Lönn M. E., Hudemann C., Lillig C. H. (2005) Thiol redox control via thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 33, 1375–1377 - PubMed
-
- Jakob U., Eser M., Bardwell J. C. A. (2000) Redox switch of Hsp33 has a novel zinc-binding motif. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 38302–38310 - PubMed
-
- Lee C., Lee S. M., Mukhopadhyay P., Kim S. J., Lee S. C., Ahn W. S., Yu M. H., Storz G., Ryu S. E. (2004) Redox regulation of OxyR requires specific disulfide bond formation involving a rapid kinetic reaction path. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11, 1179–1185 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

