Molecular weight dependent glucose lowering effect of low molecular weight Chitosan Oligosaccharide (GO2KA1) on postprandial blood glucose level in SD rats model
- PMID: 23839092
- PMCID: PMC3742240
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140714214
Molecular weight dependent glucose lowering effect of low molecular weight Chitosan Oligosaccharide (GO2KA1) on postprandial blood glucose level in SD rats model
Abstract
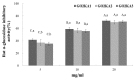
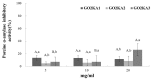
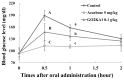
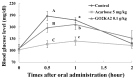
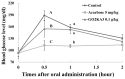
This research investigated the effect of enzymatically digested low molecular weight (MW) chitosan oligosaccharide on type 2 diabetes prevention. Three different chitosan oligosaccharide samples with varying MW were evaluated in vitro for inhibition of rat small intestinal α-glucosidase and porcine pancreatic α-amylase (GO2KA1; <1000 Da, GO2KA2; 1000-10,000 Da, GO2KA3; MW > 10,000 Da). The in vitro results showed that all tested samples had similar rat α-glucosidase inhibitory and porcine α-amylase inhibitory activity. Based on these observations, we decided to further investigate the effect of all three samples at a dose of 0.1 g/kg, on reducing postprandial blood glucose levels in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat model after sucrose loading test. In the animal trial, all tested samples had postprandial blood glucose reduction effect, when compared to control, however GO2KA1 supplementation had the strongest effect. The glucose peak (Cmax) for GO2KA1 and control was 152 mg/dL and 193 mg/dL, respectively. The area under the blood glucose-time curve (AUC) for GO2KA1 and control was 262 h mg/dL and 305 h mg/dL, respectively. Furthermore, the time of peak plasma concentration of blood glucose (Tmax) for GO2KA1 was significantly delayed (0.9 h) compared to control (0.5 h). These results suggest that GO2KA1 could have a beneficial effect for blood glucose management relevant to diabetes prevention in normal and pre-diabetic individuals. The suggested mechanism of action is via inhibition of the carbohydrate hydrolysis enzyme α-glucosidase and since GO2KA1 (MW < 1000 Da) had higher in vivo effect, we hypothesize that it is more readily absorbed and might exert further biological effect once it is absorbed in the blood stream, relevant to blood glucose management.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of long-term supplementation of low molecular weight chitosan oligosaccharide (GO2KA1) on fasting blood glucose and HbA1c in db/db mice model and elucidation of mechanism of action.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jul 29;14:272. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-272. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25074485 Free PMC article.
-
Selected coffee (Coffea arabica L.) extracts inhibit intestinal α-glucosidases activities in-vitro and postprandial hyperglycemia in SD Rats.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Sep 23;22(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03726-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 36151573 Free PMC article.
-
The Postprandial Anti-Hyperglycemic Effect of Pyridoxine and Its Derivatives Using In Vitro and In Vivo Animal Models.Nutrients. 2018 Feb 28;10(3):285. doi: 10.3390/nu10030285. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29495635 Free PMC article.
-
α-Glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitors from seed oil: A review of liposoluble substance to treat diabetes.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Nov 2;57(16):3438-3448. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2015.1129309. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 26854322 Review.
-
A Review on Experimental Models to Test Medicinal Plants on Postprandial Blood Glucose in Diabetes.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2023;19(9):e080422203278. doi: 10.2174/1573399818666220408100830. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2023. PMID: 35400346 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Chitosan Oligosaccharide in Metabolic Syndrome: A Review of Possible Mechanisms.Mar Drugs. 2021 Sep 1;19(9):501. doi: 10.3390/md19090501. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34564163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan Oligosaccharide Alleviates Abnormal Glucose Metabolism without Inhibition of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in a High-Fat Diet/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rat Model.Mar Drugs. 2021 Jun 23;19(7):360. doi: 10.3390/md19070360. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34201848 Free PMC article.
-
Single-blind, placebo controlled randomised clinical study of chitosan for body weight reduction.Nutr J. 2016 Jan 8;15:3. doi: 10.1186/s12937-016-0122-8. Nutr J. 2016. PMID: 26747458 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Developing a new multi-featured chitosan-quinoline Schiff base with potent antibacterial, antioxidant, and antidiabetic activities: design and molecular modeling simulation.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 21;13(1):22792. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50130-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38123716 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of long-term dietary arginyl-fructose (AF) on hyperglycemia and HbA1c in diabetic db/db mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 May 12;15(5):8352-9. doi: 10.3390/ijms15058352. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24823880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Center for Disease Control. [(on accessed 15 May 2011)]. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2007pdf.
-
- The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Care. 1997;20:1183–1197. - PubMed
-
- Meigs J.B., Nathan D.M., D’Agostino R.B., Sr, Wilson P.W. Framingham offspring study. Fasting and postchallenge glycemia and cardiovascular disease risk: The framingham offspring study. Diabet. Care. 2002;10:1845–1850. - PubMed
-
- Smith N.L., Barzilay J.I., Shaffer D., Savage P.J., Heckbert S.R., Kuller L.H., Kronmal R.A., Resnick H.E., Psaty B.M. Fasting and 2 hour postchallenge serum glucose measures and risk of incident cardiovascular events in the elderly: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Arch. Int. Med. 2002;162:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Coutinho M., Gerstein H.C., Wang Y., Yusuf S. The relationship between glucose and incident cardiovascular events. A metaregression analysis of published data from 20 studies of 95,783 individuals followed for 12.4 years. Diabet. Care. 1999;22:233–240. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

