KpnEF, a new member of the Klebsiella pneumoniae cell envelope stress response regulon, is an SMR-type efflux pump involved in broad-spectrum antimicrobial resistance
- PMID: 23836167
- PMCID: PMC3754300
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02284-12
KpnEF, a new member of the Klebsiella pneumoniae cell envelope stress response regulon, is an SMR-type efflux pump involved in broad-spectrum antimicrobial resistance
Abstract
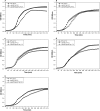
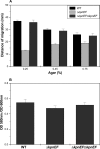
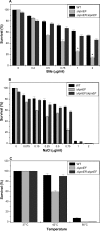
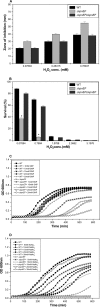
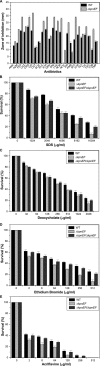
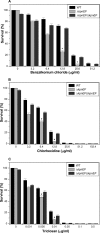
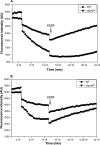
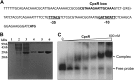
Klebsiella pneumoniae has been frequently associated with nosocomial infections. Efflux systems are ubiquitous transporters that also function in drug resistance. Genome analysis of K. pneumoniae strain NTUH-K2044 revealed the presence of ∼15 putative drug efflux systems. We discuss here for the first time the characterization of a putative SMR-type efflux pump, an ebrAB homolog (denoted here as kpnEF) with respect to Klebsiella physiology and the multidrug-resistant phenotype. Analysis of hypermucoviscosity revealed direct involvement of kpnEF in capsule synthesis. The ΔkpnEF mutant displayed higher sensitivity to hyperosmotic (∼2.8-fold) and high bile (∼4.0-fold) concentrations. Mutation in kpnEF resulted in increased susceptibility to cefepime, ceftriaxone, colistin, erythromycin, rifampin, tetracycline, and streptomycin; mutated strains changed from being resistant to being susceptible, and the resistance was restored upon complementation. The ΔkpnEF mutant displayed enhanced sensitivity toward structurally related compounds such as sodium dodecyl sulfate, deoxycholate, and dyes, including clinically relevant disinfectants such as benzalkonium chloride, chlorhexidine, and triclosan. The prevalence of kpnEF in clinical strains broadens the diversity of antibiotic resistance in K. pneumoniae. Experimental evidence of CpxR binding to the efflux pump promoter and quantification of its expression in a cpxAR mutant background demonstrated kpnEF to be a member of the Cpx regulon. This study helps to elucidate the unprecedented biological functions of the SMR-type efflux pump in Klebsiella spp.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of the two component signal transduction system CpxAR in conferring cefepime and chloramphenicol resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae NTUH-K2044.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033777. Epub 2012 Apr 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22496764 Free PMC article.
-
Role of novel multidrug efflux pump involved in drug resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae.PLoS One. 2014 May 13;9(5):e96288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096288. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24823362 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Oxidative Stress Regulon Identifies soxS as a Genetic Target for Resistance Reversal in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0086721. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00867-21. Epub 2021 Jun 8. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34098732 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of clinical isolation of drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with overexpression of OqxB efflux pump as the decisive drug resistance factor.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 3;12(10):e0012224. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00122-24. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39150249 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in Outer Membrane Permeability Favor Drug-Resistant Phenotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae.Microb Drug Resist. 2017 Jun;23(4):413-420. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2016.0017. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Microb Drug Resist. 2017. PMID: 27526080 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into Kinases of ESKAPE Pathogens for Therapeutic Interventions.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2024;22(3):276-297. doi: 10.2174/0118715257267497231128093529. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39403051 Review.
-
Polymorphic variation in susceptibility and metabolism of triclosan-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical strains obtained after exposure to biocides and antibiotics.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(6):3413-23. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00187-15. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25824225 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticle-Based Combinations with Antimicrobial Agents against Antimicrobial-Resistant Clinical Isolates.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Sep 8;11(9):1219. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11091219. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139997 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Discovery of Efflux Pump Inhibitors as Novel Potentiators to Control Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Sep 7;12(9):1417. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12091417. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic effects of polymyxin and vancomycin combinations on carbapenem- and polymyxin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and their molecular characteristics.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Dec 12;11(6):e0119923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01199-23. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37905823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alekshun MN, Levy SB. 2007. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell 128:1037–1050 - PubMed
-
- Piddock LJ. 2006. Multidrug-resistance efflux pumps: not just for resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4:629–636 - PubMed
-
- Paulsen IT. 2003. Multidrug efflux pumps and resistance: regulation and evolution. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6:446–451 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

