Beclin 1 and nuclear factor-κBp65 are upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 23833647
- PMCID: PMC3700917
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2013.1307
Beclin 1 and nuclear factor-κBp65 are upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
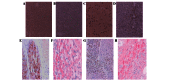
There are no sensitive and specific biomarkers that aid in the clinical diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The aim of the present study was to determine the mRNA and protein expression levels of beclin 1 (BECN1) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)p65 in patients with HCC, to evaluate their value as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization were used to detect the expression of hepatic BECN1 and NF-kBp65 in patients with HCC, hepatitis B virus (HBV) or cirrhosis, as compared with the expression levels in healthy subjects. The expression level of the BECN1 protein in the HCC tissue was significantly high compared with that in the cirrhotic, hepatitis and normal tissues. The expression of the BECN1 protein in the hepatitis tissue was significantly high compared with that of the cirrhotic and normal tissues. The expression of the BECN1 mRNA in the cancer tissue was significantly high compared with that of the cirrhotic and normal tissues, and the expression of the BECN1 mRNA in the hepatitis tissue was significantly higher than that of the cirrhotic and normal tissues. The expression of the NF-κBp65 protein in the cancer tissue was significantly high compared with that of the cirrhotic, hepatitis and normal tissues. The expression of the NF-κBp65 mRNA in-the cancer tissue was significantly high compared with that of the cirrhotic, hepatitis and normal tissues. BECN1 expression was positively correlated with NF-κBp65 expression in HCC. The abnormal expression of BECN1 and NF-κBp65 was closely associated with the development of HCC. Finally, a search in GeneGo pathway database observed a link between BECN1 and NF-κBp65 through multiple proteins. These results indicate that BECN1 and NF-κBp65 are upregulated in HCC, and that they may serve as useful biomarkers for HCC.
Keywords: beclin 1; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunohistochemistry; in situ hybridization; nuclear factor-κB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aerobic glycolysis enhances HBx-initiated hepatocellular carcinogenesis via NF-κBp65/HK2 signalling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Nov 21;41(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02531-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36411480 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of NF-κBp65 drives inflammation-mediated hepatocellular carcinogenesis and is a novel therapeutic target.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 11;40(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02062-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34380537 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of nuclear factor kappaB in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer. 2000 Dec 1;89(11):2274-81. Cancer. 2000. PMID: 11147598
-
Factors predicting occurrence and prognosis of hepatitis-B-virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Oct 14;17(38):4258-70. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i38.4258. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 22090781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What can we learn from hepatitis B virus clinical cohorts?Liver Int. 2015 Jan;35 Suppl 1:91-9. doi: 10.1111/liv.12716. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25529093 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel phloretin-based combinations targeting glucose metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma through GLUT2/PEPCK axis of action: in silico molecular modelling and in vivo studies.Med Oncol. 2023 Dec 11;41(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02236-x. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38078989
-
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2/3 interacts with p65 and stabilizes it in the cytoplasm in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2015 Oct 12;15:675. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1665-3. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26458400 Free PMC article.
-
An evidence-based update on the pharmacological activities and possible molecular targets of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Dec 17;9:33-78. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S72892. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25552899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Autophagy in the Pathogenesis of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Current Evidence and Perspectives.Curr Obes Rep. 2021 Jun;10(2):134-161. doi: 10.1007/s13679-021-00431-3. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Curr Obes Rep. 2021. PMID: 33751456 Review.
-
Suramin inhibits cell proliferation in ovarian and cervical cancer by downregulating heparanase expression.Cancer Cell Int. 2015 May 13;15:52. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0196-y. eCollection 2015. Cancer Cell Int. 2015. PMID: 26052253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Block TM, Mehta AS, Fimmel CJ, Jordan R. Molecular viral oncology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2003;22:5093–5107. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Thomas MB, Zhu AX. Hepatocellular carcinoma: the need for progress. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2892–2899. - PubMed
-
- Frenette C, Gish RG. Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular and genomic guideline for the clinician. Clin Liver Dis. 2011;15:307–321. vii–x. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
