Type 2 immunity and wound healing: evolutionary refinement of adaptive immunity by helminths
- PMID: 23827958
- PMCID: PMC3789590
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3476
Type 2 immunity and wound healing: evolutionary refinement of adaptive immunity by helminths
Abstract
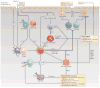
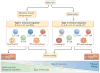
Helminth-induced type 2 immune responses, which are characterized by the T helper 2 cell-associated cytokines interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13, mediate host protection through enhanced tissue repair, the control of inflammation and worm expulsion. In this Opinion article, we consider type 2 immunity in the context of helminth-mediated tissue damage. We examine the relationship between the control of helminth infection and the mechanisms of wound repair, and we provide a new understanding of the adaptive type 2 immune response and its contribution to both host tolerance and resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: see Web version for details.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Macrophages in the Repair Process during the Tissue Migrating and Resident Helminth Infections.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:8634603. doi: 10.1155/2016/8634603. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27648452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of regulatory cells by helminth parasites: exploitation for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.Immunol Rev. 2014 May;259(1):206-30. doi: 10.1111/imr.12164. Immunol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24712468 Review.
-
Evolution of Th2 immunity: a rapid repair response to tissue destructive pathogens.PLoS Pathog. 2011 May;7(5):e1002003. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002003. Epub 2011 May 12. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21589896 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cytokines and beyond: Regulation of innate immune responses during helminth infection.Cytokine. 2020 Sep;133:154527. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.08.021. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 30241895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural helper cells: a new player in the innate immune response against helminth infection.Adv Immunol. 2010;108:21-44. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380995-7.00002-1. Adv Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21056728
Cited by
-
Type 2 responses at the interface between immunity and fat metabolism.Curr Opin Immunol. 2015 Oct;36:67-72. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26204571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Scaffold Immune Microenvironment: Biomaterial-Mediated Immune Polarization in Traumatic and Nontraumatic Applications<sup/>Tissue Eng Part A. 2017 Oct;23(19-20):1044-1053. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2016.0304. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017. PMID: 27736323 Free PMC article.
-
Basophils prime group 2 innate lymphoid cells for neuropeptide-mediated inhibition.Nat Immunol. 2020 Oct;21(10):1181-1193. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0753-y. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Nat Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32807943 Free PMC article.
-
Paneth Cell-Derived Lysozyme Defines the Composition of Mucolytic Microbiota and the Inflammatory Tone of the Intestine.Immunity. 2020 Aug 18;53(2):398-416.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.07.010. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32814028 Free PMC article.
-
Unique adipose tissue invariant natural killer T cell subpopulations control adipocyte turnover in mice.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 21;14(1):8512. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44181-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38129377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artis D, Maizels RM, Finkelman FD. Forum: Immunology: Allergy challenged. Nature. 2012;484:458–459. - PubMed
-
- Deter J, Cosson JF, Chaval Y, Charbonnel N, Morand S. The intestinal nematode Trichuris arvicolae affects the fecundity of its host, the common vole Microtus arvalis. Parasitol Res. 2007;101:1161–1164. - PubMed
-
- Coop RL, Kyriazakis I. Influence of host nutrition on the development and consequences of nematode parasitism in ruminants. Trends Parasitol. 2001;17:325–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

