Prognostic significance of HIF-1α expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 23799043
- PMCID: PMC3683060
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065753
Prognostic significance of HIF-1α expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: Pilot studies have evaluated the correlation between hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) overexpression and clinical outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. However, the results remain inconclusive. To comprehensively and quantitatively summarize the evidence on the suitability of HIF-1α to predict the prognosis of patients with HCC, a meta-analysis was carried out.
Methods: Systematic literature searches were applied to PubMed, Elsevier and Web of Science databases until Feb. 2013. Seven studies (953 patients) were included in this meta-analysis. Pooled measure was calculated from the available data to evaluate the association between tissue -based HIF-1α level and overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in HCC patients. The relation between HIF-1α expression and vascular invasion was also assessed. Data were synthesized with fixed or random effect model, hazard ration (HR) or odds ratio (OR) with its 95% confidence interval (CI) was used as the effect size estimate.
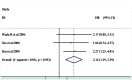
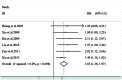
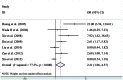
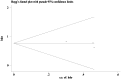
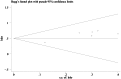
Result: The combined data suggested that HIF-1α overexpression in HCC correlated with poor OS [HR = 1.65 (95% (CI): 1.38, 1.97)] and DFS [HR = 2.14 (95% CI: 1.39, 3.29)]. And high HIF-1α expression tended to be associated with vascular invasion [OR = 2.21 (95% CI: 1.06, 4.57)].
Conclusion: HIF-1α overexpression indicates a poor prognosis for patients with HCC, it may also have predictive potential for HCC invasion and metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and hypoxia-inducible factor-2α overexpression on hepatocellular carcinoma survival: A systematic review with meta-analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jun;36(6):1487-1496. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15395. Epub 2021 Jan 26. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33393670
-
Elevated LncRNA TRERNA1 correlated with activation of HIF-1α predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 Nov;227:153612. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153612. Epub 2021 Sep 11. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 34560417
-
Hypoxia inducible factor 1α in hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis: Association with prognosis.Pathol Res Pract. 2018 Dec;214(12):1987-1992. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Pathol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30274686
-
Protein expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct;38(5):598-603. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 May 15. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24835771 Review.
-
Association of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression with susceptibility to hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Int J Biol Markers. 2023 Dec;38(3-4):149-158. doi: 10.1177/03936155231204391. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Int J Biol Markers. 2023. PMID: 37787154 Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of immunohistochemical expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α as a prognostic role in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jan 28;20(4):1107-13. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i4.1107. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24574785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2 is the key to chemotherapy resistance in MCF7 breast cancer cells under hypoxia.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):14659-72. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7406. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26894974 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and Cancer.Curr Sleep Med Rep. 2017 Mar;3(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s40675-017-0062-7. Epub 2017 Jan 28. Curr Sleep Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28944164 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmodium infection downregulates hypoxia‑inducible factor 1α expression to suppress the vascularization and tumorigenesis of liver cancer.Oncol Lett. 2024 Oct 14;28(6):604. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14737. eCollection 2024 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39483968 Free PMC article.
-
Asparagus Polysaccharide inhibits the Hypoxia-induced migration, invasion and angiogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells partly through regulating HIF1α/VEGF expression via MAPK and PI3K signaling pathway.J Cancer. 2021 May 10;12(13):3920-3929. doi: 10.7150/jca.51407. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34093799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Filmus J, Capurro M (2004) Glypican-3 and alphafetoprotein as diagnostic tests for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Diagn 8: 207–212. - PubMed
-
- Harris AL (2002) Hypoxia–a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 38–47. - PubMed
-
- Kimura S, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, Kuwai T, Hihara J, et al. (2004) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and tumour angiogenesis in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 40: 1904–1912. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

