XBP-1 is a cell-nonautonomous regulator of stress resistance and longevity
- PMID: 23791175
- PMCID: PMC4771415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.042
XBP-1 is a cell-nonautonomous regulator of stress resistance and longevity
Abstract
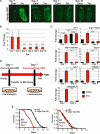
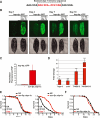
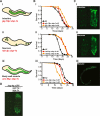
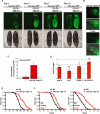
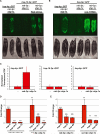
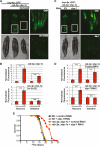
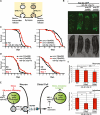
The ability to ensure proteostasis is critical for maintaining proper cell function and organismal viability but is mitigated by aging. We analyzed the role of the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response (UPR(ER)) in aging of C. elegans and found that age-onset loss of ER proteostasis could be reversed by expression of a constitutively active form of XBP-1, XBP-1s. Neuronally derived XBP-1s was sufficient to rescue stress resistance, increase longevity, and activate the UPR(ER) in distal, non-neuronal cell types through a cell-nonautonomous mechanism. Loss of UPR(ER) signaling components in distal cells blocked cell-nonautonomous signaling from the nervous system, thereby blocking increased longevity of the entire animal. Reduction of small clear vesicle (SCV) release blocked nonautonomous signaling downstream of xbp-1s, suggesting that the release of neurotransmitters is required for this intertissue signaling event. Our findings point toward a secreted ER stress signal (SERSS) that promotes ER stress resistance and longevity.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Protein metabolism: Proteostasis goes global.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;14(8):461. doi: 10.1038/nrm3626. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23839579 No abstract available.
-
Commentary: XBP-1 Is a Cell-Nonautonomous Regulator of Stress Resistance and Longevity.Front Aging Neurosci. 2016 Aug 3;8:182. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00182. eCollection 2016. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27534903 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Tyramine Acts Downstream of Neuronal XBP-1s to Coordinate Inter-tissue UPRER Activation and Behavior in C. elegans.Dev Cell. 2020 Dec 21;55(6):754-770.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.10.024. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Dev Cell. 2020. PMID: 33232669 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal XBP-1 Activates Intestinal Lysosomes to Improve Proteostasis in C. elegans.Curr Biol. 2019 Jul 22;29(14):2322-2338.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.06.031. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31303493 Free PMC article.
-
Four glial cells regulate ER stress resistance and longevity via neuropeptide signaling in C. elegans.Science. 2020 Jan 24;367(6476):436-440. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz6896. Science. 2020. PMID: 31974253 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of protein homeostasis in glia extends lifespan in C. elegans.Exp Neurol. 2021 May;339:113648. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113648. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33600813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Nonautonomous Mechanisms Underlying Cellular and Organismal Aging.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2016;321:259-97. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2015.09.003. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26811290 Review.
Cited by
-
Two Conserved Histone Demethylases Regulate Mitochondrial Stress-Induced Longevity.Cell. 2016 May 19;165(5):1209-1223. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.012. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27133168 Free PMC article.
-
The UPR in Neurodegenerative Disease: Not Just an Inside Job.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 22;10(8):1090. doi: 10.3390/biom10081090. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32707908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
APP-Induced Patterned Neurodegeneration Is Exacerbated by APOE4 in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Aug 5;10(8):2851-2861. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401486. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32580938 Free PMC article.
-
Knock-down of transcription factor skinhead-1 exacerbates arsenite-induced oxidative damage in Caenorhabditis elegans.Biometals. 2021 Jun;34(3):675-686. doi: 10.1007/s10534-021-00303-2. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Biometals. 2021. PMID: 33881688
-
ER-phagy drives age-onset remodeling of endoplasmic reticulum structure-function and lifespan.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 8:2024.08.07.607085. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.07.607085. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39149405 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Acosta-Alvear D, Zhou Y, Blais A, Tsikitis M, Lents NH, Arias C, Lennon CJ, Kluger Y, Dynlacht BD. XBP1 controls diverse cell type- and condition-specific transcriptional regulatory networks. Mol. Cell. 2007;27:53–66. - PubMed
-
- Alcedo J, Kenyon C. Regulation of C. elegans longevity by specific gustatory and olfactory neurons. Neuron. 2004;41:45–55. - PubMed
-
- Apfeld J, Kenyon C. Regulation of lifespan by sensory perception in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1999;402:804–809. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

