Q-TWiST analysis comparing ipilimumab/dacarbazine vs placebo/dacarbazine for patients with stage III/IV melanoma
- PMID: 23787916
- PMCID: PMC3708560
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.298
Q-TWiST analysis comparing ipilimumab/dacarbazine vs placebo/dacarbazine for patients with stage III/IV melanoma
Abstract
Background: Study CA184024 was a multinational, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study comparing ipilimumab/dacarbazine (DTIC) vs placebo/DTIC in patients with untreated stage III/IV melanoma, which showed that ipilimumab significantly improves survival in patients with metastatic melanoma. The objective of this analysis was to compare the quality-adjusted survival experience among patients in this trial.
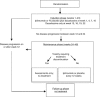
Methods: Survival time was partitioned into health states: toxicity, time before progression without toxicity, and relapse until death or end of follow-up. Q-TWiST (quality-adjusted time without symptoms of disease or toxicity of treatment) was calculated as the utility-weighted sum of the mean health state durations. Analyses were repeated over extended follow-up periods.
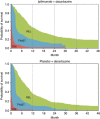
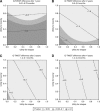
Results: Based on a combination of trial-based and external utility scores, the Q-TWiST difference in this trial was 0.50 months (P=0.0326) favoring ipilimumab after 1 year. The Q-TWiST difference was 1.5 months with 2 years of follow-up (P=0.0091), 2.36 months at 3 years (P=0.005) and 3.28 months at 4 years (P=0.0074).
Conclusion: During the first year of study, there was little difference between groups in quality-adjusted survival. However, after 2, 3 and 4 years follow-up for patients with extended survival, the benefits of IPI+DTIC vs PLA+DTIC for advanced melanoma continue to accrue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quality-adjusted survival of nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab alone versus ipilimumab alone among treatment-naive patients with advanced melanoma: a quality-adjusted time without symptoms or toxicity (Q-TWiST) analysis.Qual Life Res. 2019 Jan;28(1):109-119. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-1984-3. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Qual Life Res. 2019. PMID: 30191365 Clinical Trial.
-
Ipilimumab for Previously Untreated Unresectable Malignant Melanoma: A Critique of the Evidence.Pharmacoeconomics. 2015 Dec;33(12):1269-79. doi: 10.1007/s40273-015-0299-2. Pharmacoeconomics. 2015. PMID: 26043718 Review.
-
Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma.N Engl J Med. 2011 Jun 30;364(26):2517-26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1104621. Epub 2011 Jun 5. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21639810 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase II multicenter study of ipilimumab with or without dacarbazine in chemotherapy-naïve patients with advanced melanoma.Invest New Drugs. 2011 Jun;29(3):489-98. doi: 10.1007/s10637-009-9376-8. Epub 2010 Jan 16. Invest New Drugs. 2011. PMID: 20082117 Clinical Trial.
-
Ipilimumab: showing survival benefit in metastatic melanoma.Future Oncol. 2011 Nov;7(11):1255-64. doi: 10.2217/fon.11.105. Future Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22044200 Review.
Cited by
-
[Abscopal effect in the treatment of malignant melanoma].Hautarzt. 2015 Jul;66(7):545-8. doi: 10.1007/s00105-014-3567-8. Hautarzt. 2015. PMID: 25576145 German.
-
Targeting immune checkpoints in unresectable metastatic cutaneous melanoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 agents trials.Cancer Med. 2016 Jul;5(7):1481-91. doi: 10.1002/cam4.732. Epub 2016 May 11. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27167347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination Therapy with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors or Alkylating Agents.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Jul 22;16:855-869. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S464245. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 39072340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dacarbazine combined targeted therapy versus dacarbazine alone in patients with malignant melanoma: a meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 11;9(12):e111920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111920. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25502446 Free PMC article.
-
A practical guide to understanding, using and including patient reported outcomes in clinical trials in ovarian cancer.J Gynecol Oncol. 2018 Sep;29(5):e81. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2018.29.e81. Epub 2018 Jun 9. J Gynecol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30022641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agarwala SS. Current systemic therapy for metastatic melanoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009;9:587–595. - PubMed
-
- Attia P, Phan GQ, Maker AV, Robinson MR, Quezado MM, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Topalian SL, Kammula US, Royal RE, Restifo NP, Haworth LR, Levy C, Mavroukakis SA, Nichol G, Yellin MJ, Rosenberg SA. Autoimmunity correlates with tumor regression in patients with metastatic melanoma treated with anti–cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23 (25:6043–6053. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batty AJ, Fisher D, Winn B, Wang Q, Tolley K, Rowen D. Estimating quality of life in advanced melanoma; a comparison of standard gamble, SF-36 mapped, and EORTC QLQ-C30 mapped utilities. Value Health. 2011;14:A461–A462.
-
- Cole BF, Gelber RD, Anderson KM, International Breast Cancer Study Group Parametric approaches to quality-adjusted survival analysis. Biometrics. 1994;50:621–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

