A brief history of triplet repeat diseases
- PMID: 23754215
- PMCID: PMC3913379
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-411-1_1
A brief history of triplet repeat diseases
Abstract
Instability of repetitive DNA sequences within the genome is associated with a number of human diseases. The expansion of trinucleotide repeats is recognized as a major cause of neurological and neuromuscular diseases, and progress in understanding the mutations over the last 20 years has been substantial. Here we provide a brief summary of progress with an emphasis on technical advances at different stages.
Figures
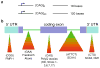
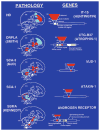
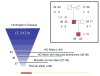

Similar articles
-
Trinucleotide expansion in disease: why is there a length threshold?Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014 Jun;26:131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014. PMID: 25282113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances in understanding of clinical presentations and molecular mechanisms of triplet repeat diseases].Nihon Rinsho. 1999 Apr;57(4):778-86. Nihon Rinsho. 1999. PMID: 10222765 Review. Japanese.
-
Role of noncoding RNAs in trinucleotide repeat neurodegenerative disorders.Exp Neurol. 2012 Jun;235(2):469-75. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.01.019. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22309832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Genomic instability and neurodegenerative disease].Rinsho Byori. 1999 Jan;47(1):37-45. Rinsho Byori. 1999. PMID: 10067364 Japanese.
-
Progress on the mechanistic research of the trinucleotide repeat instabilities underlying human neurodegenerative diseases.Yi Chuan. 2021 Sep 20;43(9):835-848. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.21-182. Yi Chuan. 2021. PMID: 34702697 Review.
Cited by
-
How a homolog of high-fidelity replicases conducts mutagenic DNA synthesis.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;22(4):298-303. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2985. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25775266 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput techniques enable advances in the roles of DNA and RNA secondary structures in transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation.Genome Biol. 2022 Jul 18;23(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02727-6. Genome Biol. 2022. PMID: 35851062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simulation-guided tunable DNA probe design for mismatch tolerant hybridization.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 22;19(8):e0305002. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305002. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39172820 Free PMC article.
-
Big versus small: The impact of aggregate size in disease.Protein Sci. 2023 Jul;32(7):e4686. doi: 10.1002/pro.4686. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37243896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-depth, high-accuracy microsatellite genotyping enables precision lung cancer risk classification.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 16;36(46):6383-6390. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.256. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28759038 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS062384/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS060115/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AG00266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA092584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS069177/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 NS069177/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM066359/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS060115/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES020766/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS040738/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS40738/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS062384/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

