Active suppression induced by repetitive self-epitopes protects against EAE development
- PMID: 23738007
- PMCID: PMC3667816
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064888
Active suppression induced by repetitive self-epitopes protects against EAE development
Abstract
Background: Autoimmune diseases result from a breakdown in self-tolerance to autoantigens. Self-tolerance is induced and sustained by central and peripheral mechanisms intended to deviate harmful immune responses and to maintain homeostasis, where regulatory T cells play a crucial role. The use of self-antigens in the study and treatment of a range of autoimmune diseases has been widely described; however, the mechanisms underlying the induced protection by these means are unclear. This study shows that protection of experimental autoimmune disease induced by T cell self-epitopes in a multimerized form (oligomers) is mediated by the induction of active suppression.
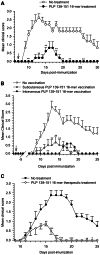
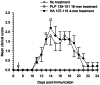
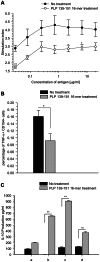
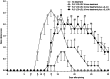
Principal findings: The experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) animal model for multiple sclerosis was used to study the mechanisms of protection induced by the treatment of oligomerized T cell epitope of myelin proteolipid protein (PLP139-151). Disease protection attained by the administration of oligomers was shown to be antigen specific and effective in both prevention and treatment of ongoing EAE. Oligomer mediated tolerance was actively transferred by cells from treated mice into adoptive hosts. The induction of active suppression was correlated with the recruitment of cells in the periphery associated with increased production of IL-10 and reduction of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α. The role of suppressive cytokines was demonstrated by the reversion of oligomer-induced protection after in vivo blocking of either IL-10 or TGF-β cytokines.
Conclusions: This study strongly supports an immunosuppressive role of repeat auto-antigens to control the development of EAE with potential applications in vaccination and antigen specific treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pathologic role and temporal appearance of newly emerging autoepitopes in relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2000 Jan 15;164(2):670-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.2.670. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10623809
-
Expansion by self antigen is necessary for the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by T cells primed with a cross-reactive environmental antigen.J Immunol. 1998 Oct 1;161(7):3307-14. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9759846
-
Targeting DEC-205-DCIR2+ dendritic cells promotes immunological tolerance in proteolipid protein-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Mol Med. 2018 May 3;24(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s10020-018-0017-6. Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30134798 Free PMC article.
-
T cell response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE): role of self and cross-reactive antigens in shaping, tuning, and regulating the autopathogenic T cell repertoire.Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:101-23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.081701.141316. Epub 2001 Oct 4. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11861599 Review.
-
Tolerance in the absence of autoantigen.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2007 Sep;7(3):203-10. doi: 10.2174/187153007781662549. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17897047 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Infusion of Sulfosuccinimidyl-4-[N-maleimidomethyl]cyclohexane-1-carboxylate-Conjugated MOG35-55-Coupled Spleen Cells Effectively Prevents and Reverses Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in Mice.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:129682. doi: 10.1155/2015/129682. Epub 2015 Jul 14. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26258148 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Modulation and Prevention of Autoimmune Disease by Repeated Sequences from Parasites Linked to Self Antigens.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;11(4):749-762. doi: 10.1007/s11481-016-9701-x. Epub 2016 Aug 12. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27518777
-
The Short and Long-Term Effects of Pregnancy on Multiple Sclerosis and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.J Clin Med. 2018 Nov 28;7(12):494. doi: 10.3390/jcm7120494. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30486504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerogenic Immunomodulation by PEGylated Antigenic Peptides.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 9;11:529035. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.529035. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33162973 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-1 is essential for the induction of MOG35-55 -based intravenous tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Eur J Immunol. 2016 Jul;46(7):1783-96. doi: 10.1002/eji.201546212. Epub 2016 May 25. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27151444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watanabe K, Sukumaran V, Veeraveedu PT, Thandavarayan RA, Gurusamy N, et al. (2011) Regulation of inflammation and myocardial fibrosis in experimental autoimmune myocarditis. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 10: 218–225. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, Harris PE, Colovai AI, Reed EF, Maffei A, et al. (1995) Suppression of the indirect pathway of T cell reactivity by high doses of allopeptide. Autoimmunity 21: 173–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

