Signal integration by mTORC1 coordinates nutrient input with biosynthetic output
- PMID: 23728461
- PMCID: PMC3743096
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2763
Signal integration by mTORC1 coordinates nutrient input with biosynthetic output
Abstract
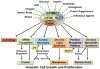
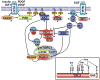
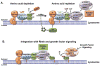
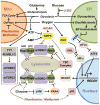
Flux through metabolic pathways is inherently sensitive to the levels of specific substrates and products, but cellular metabolism is also managed by integrated control mechanisms that sense the nutrient and energy status of a cell or organism. The mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a protein kinase complex ubiquitous to eukaryotic cells, has emerged as a critical signalling node that links nutrient sensing to the coordinated regulation of cellular metabolism. Here, we discuss the role of mTORC1 as a conduit between cellular growth conditions and the anabolic processes that promote cell growth. The emerging network of signalling pathways through which mTORC1 integrates systemic signals (secreted growth factors) with local signals (cellular nutrients - amino acids, glucose and oxygen - and energy, ATP) is detailed. Our expanding understanding of the regulatory network upstream of mTORC1 provides molecular insights into the integrated sensing mechanisms by which diverse cellular signals converge to control cell physiology.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests related to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutrient signaling to mTOR and cell growth.Trends Biochem Sci. 2013 May;38(5):233-42. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013. PMID: 23465396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutrient regulation of the mTOR complex 1 signaling pathway.Mol Cells. 2013 Jun;35(6):463-73. doi: 10.1007/s10059-013-0138-2. Epub 2013 May 20. Mol Cells. 2013. PMID: 23694989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular basis of nutrient sensing and signalling by mTORC1 in metabolism regulation and disease.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Dec;24(12):857-875. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00641-8. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37612414 Review.
-
mTORC1 signaling and the metabolic control of cell growth.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017 Apr;45:72-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.02.012. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28411448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SLC38A9: A lysosomal amino acid transporter at the core of the amino acid-sensing machinery that controls MTORC1.Autophagy. 2016 Jun 2;12(6):1061-2. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1091143. Epub 2015 Oct 2. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 26431368 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Polarization of M2 macrophages requires Lamtor1 that integrates cytokine and amino-acid signals.Nat Commun. 2016 Oct 12;7:13130. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13130. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27731330 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α links palmitate-induced mTOR activation and lipotoxicity in hepatocytes.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):C1130-C1140. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00165.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33052067 Free PMC article.
-
Intrahippocampal glutamine administration inhibits mTORC1 signaling and impairs long-term memory.Learn Mem. 2015 Apr 15;22(5):239-46. doi: 10.1101/lm.038265.115. Print 2015 May. Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 25878136 Free PMC article.
-
Fundamentals of cancer metabolism.Sci Adv. 2016 May 27;2(5):e1600200. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1600200. eCollection 2016 May. Sci Adv. 2016. PMID: 27386546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Point mutations of the mTOR-RHEB pathway in renal cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Jul 20;6(20):17895-910. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4963. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26255626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weichhart T, Saemann MD. The multiple facets of mTOR in immunity. Trends Immunol. 2009;30:218–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

