XRCC1 gene polymorphisms and the risk of differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC): a meta-analysis of case-control studies
- PMID: 23717668
- PMCID: PMC3661468
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064851
XRCC1 gene polymorphisms and the risk of differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC): a meta-analysis of case-control studies
Abstract
Background: Previous studies investigating the association between X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 (XRCC1) polymorphisms and thyroid cancer risk have yielded inconsistent results. This meta-analysis was performed to derive a more precise estimation of the relationship between three XRCC1 polymorphisms and thyroid cancer risk.
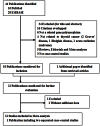
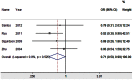
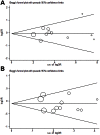
Methods/principal findings: PubMed and EMBASE database were systematically searched to identify relevant studies. 10 publications were selected for this meta-analysis, including 11 studies for Arg399Gln polymorphism (1726 cases and 3774 controls), 7 studies for Arg194Trp polymorphism (1037 cases and 2487 controls) and 8 studies for Arg280His polymorphism (1432 cases and 3356 controls). The results in total population did not show any significant association between these three polymorphisms and the risk of DTC for all genetic models. However, when stratified by ethnicity, the results showed that Arg280His polymorphism was associated with an increased risk of DTC among Caucasians (Arg/His vs. Arg/Arg: OR = 1.45, 95% CI = 1.09-1.93; dominant model: OR = 1.43, 95% CI = 1.08-1.89; additive model: OR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.05-1.80), whereas individuals carrying Arg/His genotype have a significantly reduced risk of DTC among Asians (Arg/His vs. Arg/Arg: OR = 0.71, 95% CI = 0.51-0.98). We also detected that 399Gln variant allele carriers might presented an overall decreased risk of DTC in mixed population. Furthermore, subgroup analyses by histological subtype revealed that Arg194Trp polymorphism was significantly associated with reduced risk for papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) (dominant model: OR = 0.71, 95% CI = 0.50-0.99).
Conclusions: This meta-analysis suggests that Arg280His polymorphism might contribute to the susceptibility of DTC among Caucasians, whereas it might provide protective effects in Asians against the risk of DTC. Additionally, our results support the protective role of Arg194Trp polymorphism in developing PTC, and show evidence of an association between Arg399Gln polymorphism and decreased risk of DTC in mixed population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Associations between XRCC1 Arg399Gln, Arg194Trp, and Arg280His polymorphisms and risk of differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(9):5483-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.9.5483. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24175846
-
Association between the XRCC1 polymorphisms and glioma risk: a meta-analysis of case-control studies.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055597. Epub 2013 Jan 30. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383237 Free PMC article.
-
No association between XRCC1 genetic polymorphisms and differentiated thyroid carcinoma risk: a meta-analysis.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Nov;41(11):7613-21. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3651-2. Epub 2014 Aug 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25086624
-
X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 (XRCC1) genetic polymorphisms and cervical cancer risk: a huge systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44441. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044441. Epub 2012 Sep 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 polymorphisms and hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug 21;18(31):4207-14. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4207. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22919255 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cooperation between oncogenic Ras and wild-type p53 stimulates STAT non-cell autonomously to promote tumor radioresistance.Commun Biol. 2021 Mar 19;4(1):374. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01898-5. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33742110 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of therapeutic resistance in cancer (stem) cells with emphasis on thyroid cancer cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Mar 25;5:37. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00037. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24723911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between expression of XRCC1 and tumor proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis in glioma.Invest New Drugs. 2019 Aug;37(4):646-657. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0667-9. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Invest New Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30328556
-
GA Genotype of the Arg280His Polymorphism on The XRCC1 Gene: Genetic Susceptibility Genotype in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinomas?Balkan J Med Genet. 2021 Jul 27;24(1):73-80. doi: 10.2478/bjmg-2021-0003. eCollection 2021 Jun. Balkan J Med Genet. 2021. PMID: 34447662 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the XRCC1 polymorphisms and thyroid cancer risk: a meta-analysis from case-control studies.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 11;9(9):e87764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087764. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25211472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen AY, Jemal A, Ward EM (2009) Increasing incidence of differentiated thyroid cancer in the United States, 1988-2005. Cancer 115: 3801–3807. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, et al. (2008) Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58: 71–96. - PubMed
-
- Tronko MD, Howe GR, Bogdanova TI, Bouville AC, Epstein OV, et al. (2006) A cohort study of thyroid cancer and other thyroid diseases after the chornobyl accident: thyroid cancer in Ukraine detected during first screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 98: 897–903. - PubMed
-
- Xiong P, Zheng R, Wang LE, Bondy ML, Shen H, et al. (2005) A pilot case-control study of gamma-radiation sensitivity and risk of papillary thyroid cancer. Thyroid 15: 94–99. - PubMed
-
- Wood RD, Mitchell M, Sgouros J, Lindahl T (2001) Human DNA repair genes. Science 291: 1284–1289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

