The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century
- PMID: 23713126
- PMCID: PMC3682748
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0164
The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century
Abstract
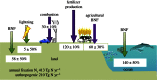
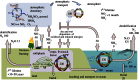
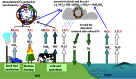
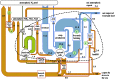
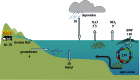
Global nitrogen fixation contributes 413 Tg of reactive nitrogen (Nr) to terrestrial and marine ecosystems annually of which anthropogenic activities are responsible for half, 210 Tg N. The majority of the transformations of anthropogenic Nr are on land (240 Tg N yr(-1)) within soils and vegetation where reduced Nr contributes most of the input through the use of fertilizer nitrogen in agriculture. Leakages from the use of fertilizer Nr contribute to nitrate (NO3(-)) in drainage waters from agricultural land and emissions of trace Nr compounds to the atmosphere. Emissions, mainly of ammonia (NH3) from land together with combustion related emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), contribute 100 Tg N yr(-1) to the atmosphere, which are transported between countries and processed within the atmosphere, generating secondary pollutants, including ozone and other photochemical oxidants and aerosols, especially ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) and ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4. Leaching and riverine transport of NO3 contribute 40-70 Tg N yr(-1) to coastal waters and the open ocean, which together with the 30 Tg input to oceans from atmospheric deposition combine with marine biological nitrogen fixation (140 Tg N yr(-1)) to double the ocean processing of Nr. Some of the marine Nr is buried in sediments, the remainder being denitrified back to the atmosphere as N2 or N2O. The marine processing is of a similar magnitude to that in terrestrial soils and vegetation, but has a larger fraction of natural origin. The lifetime of Nr in the atmosphere, with the exception of N2O, is only a few weeks, while in terrestrial ecosystems, with the exception of peatlands (where it can be 10(2)-10(3) years), the lifetime is a few decades. In the ocean, the lifetime of Nr is less well known but seems to be longer than in terrestrial ecosystems and may represent an important long-term source of N2O that will respond very slowly to control measures on the sources of Nr from which it is produced.
Keywords: denitrification; deposition; emissions; global budgets; nitrogen fixation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impacts of reactive nitrogen on climate change in China.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 29;5:8118. doi: 10.1038/srep08118. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25631557 Free PMC article.
-
Centennial-scale analysis of the creation and fate of reactive nitrogen in China (1910-2010).Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 5;110(6):2052-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221638110. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23341613 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of atmospheric ammonia (NH3) on terrestrial vegetation: a review.Environ Pollut. 2003;124(2):179-221. doi: 10.1016/s0269-7491(02)00434-7. Environ Pollut. 2003. PMID: 12713921 Review.
-
Terrestrial nitrogen-carbon cycle interactions at the global scale.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 May 27;368(1621):20130125. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0125. Print 2013 Jul 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23713123 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental impacts of nitrogen emissions in China and the role of policies in emission reduction.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2020 Oct 30;378(2183):20190324. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2019.0324. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2020. PMID: 32981443 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ammonia-oxidizing archaea are integral to nitrogen cycling in a highly fertile agricultural soil.ISME Commun. 2021 Jun 1;1(1):19. doi: 10.1038/s43705-021-00020-4. ISME Commun. 2021. PMID: 37938645 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the iron nitrogenase complex.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Jan;31(1):150-158. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01124-2. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38062208 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive Raman Gas Spectroscopy for Dinitrogen Sensing at the Parts-per-Billion Level.Anal Chem. 2024 Sep 17;96(37):14884-14890. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c02828. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39231523
-
Diazotrophic abundance and community structure associated with three meadow plants on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1292860. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1292860. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38260880 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomy of Summertime Upslope Events in Northeastern Colorado: Ammonia (NH3) Transport to the Rocky Mountains.Environ Sci Technol. 2024 Sep 11;58(38):16922-30. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c10902. Online ahead of print. Environ Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39260444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galloway JN, et al. 2004. Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry 70, 153–22610.1007/s10533-004-0370-0 (doi:10.1007/s10533-004-0370-0) - DOI - DOI
-
- Galloway JN, Aber JD, Erisman JW, Seitzinger SP, Howarth RW, Cowling EB, Cosby BJ. 2003. The nitrogen cascade. BioScience 53, 341–35610.1641/0006-3568(2003)053[0341:TNC]2.0.CO;2 (doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2003)053[0341:TNC]2.0.CO;2) - DOI - DOI
-
- Wayne RP. 1991. Chemistry of atmospheres, 2nd edn Oxford, UK: Clarendon Press
-
- Isaksen ISA, et al. 2009. Atmospheric composition change: climate–chemistry interactions. Atmos. Environ. 43, 5138–519210.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.08.003 (doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.08.003) - DOI - DOI
-
- Erisman JW, Sutton MA, Galloway J, Klimont Z, Winiwarter W. 2008. How a century of ammonia synthesis changed the world. Nat. Geosci. 1, 636–63910.1038/ngeo325 (doi:10.1038/ngeo325) - DOI - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

