Comparative analysis of 4C-Seq data generated from enzyme-based and sonication-based methods
- PMID: 23705979
- PMCID: PMC3679908
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-345
Comparative analysis of 4C-Seq data generated from enzyme-based and sonication-based methods
Abstract
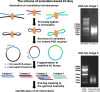
Background: Circular chromosome conformation capture, when coupled with next-generation sequencing (4C-Seq), can be used to identify genome-wide interaction of a given locus (a "bait" sequence) with all of its interacting partners. Conventional 4C approaches used restriction enzyme digestion to fragment chromatin, and recently sonication approach was also applied for this purpose. However, bioinformatics pipelines for analyzing sonication-based 4C-Seq data are not well developed. In addition, data consistency as well as similarity between the two methods has not been explored previously. Here we present a comparative analysis of 4C-Seq data generated by both methods, using an enhancer element of Pou5f1 gene in mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells.
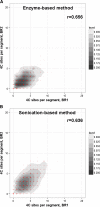
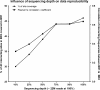
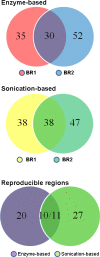
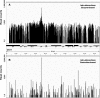
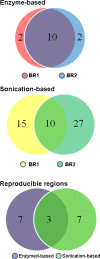
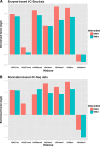
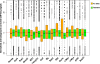
Results: From biological replicates, we found good correlation (r>0.6) for inter-chromosomal interactions identified in either enzyme or sonication method. Compared to enzyme approach, sonication method generated less distal intra-chromosomal interactions, possibly due to the difference in chromatin fragmentation. From all mapped interactions, we further applied statistical models to identify enriched interacting regions. Interestingly, data generated from the two methods showed 30% overlap of the reproducible interacting regions. The interacting sites in the reproducible regions from both methods are similarly enriched with active histone marks. In addition, the interacting sites identified from sonication-based data are enriched with ChIP-Seq signals of transcription factors Oct4, Klf4, Esrrb, Tcfcp2i1, and Zfx that are critical for reprogramming and pluripotency.
Conclusions: Both enzyme-based and sonication-based 4C-Seq methods are valuable tools to explore long-range chromosomal interactions. Due to the nature of sonication-based method, correlation analysis of the 4C interactions with transcription factor binding should be more straightforward.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of a transgenic Oct4 enhancer reveals high fidelity long-range chromosomal interactions.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 5;5:14558. doi: 10.1038/srep14558. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26435056 Free PMC article.
-
Klf4 organizes long-range chromosomal interactions with the oct4 locus in reprogramming and pluripotency.Cell Stem Cell. 2013 Jul 3;13(1):36-47. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Cell Stem Cell. 2013. PMID: 23747203
-
Analysis of 4C-seq data: A comparison of methods.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2020 Feb;18(1):2050001. doi: 10.1142/S0219720020500018. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32336253
-
Role of ChIP-seq in the discovery of transcription factor binding sites, differential gene regulation mechanism, epigenetic marks and beyond.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(18):2847-52. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.949201. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studying the epigenome using next generation sequencing.J Med Genet. 2011 Nov;48(11):721-30. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100242. Epub 2011 Aug 8. J Med Genet. 2011. PMID: 21825079 Review.
Cited by
-
w4CSeq: software and web application to analyze 4C-seq data.Bioinformatics. 2016 Nov 1;32(21):3333-3335. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw408. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27378289 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the permeability of landscape features to animal movement: using genetic structure to infer functional connectivity.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 26;10(2):e0117500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117500. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25719366 Free PMC article.
-
Biological implications and regulatory mechanisms of long-range chromosomal interactions.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 2;288(31):22369-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R113.485292. Epub 2013 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23779110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4C-seq revealed long-range interactions of a functional enhancer at the 8q24 prostate cancer risk locus.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 3;6:22462. doi: 10.1038/srep22462. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26934861 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring high-resolution chromatin interaction changes and functional enhancers of myogenic marker genes during myogenic differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2022 Aug;298(8):102149. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102149. Epub 2022 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35787372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dekker J, Rippe K, Dekker M, Kleckner N. Capturing chromosome conformation. Science. 2002;295:1306–1311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

